The Acrocanthosaurus, with a name that evokes images of towering spines, is a dinosaur that has captivated the imaginations of paleontologists and dinosaur enthusiasts alike. This formidable creature, whose name translates to ‘High-spined lizard’, roamed the Earth during the Early Cretaceous period, leaving behind a legacy that continues to intrigue us today.
Acrocanthosaurus Key Facts
| Key Fact | Detail |
|---|---|
| Acrocanthosaurus pronunciation | a-krow-kan-thuh-saw-ruhs |
| Meaning of Name | High-spined Lizard |
| Group | Theropod |
| Type Species | Acrocanthosaurus atokensis |
| Diet | Carnivore |
| When it Lived | 122.46 to 100.5 MYA |
| Period | Early Cretaceous |
| Epoch | Late/Upper Aptian to Albian |
| Length | 36.0 to 40.0 ft |
| Height | 13.0 ft |
| Weight | 3.0 to 4.0 tons |
| Mobility | Moved on two legs |
| First Discovery | 1940 by J. Willis Stovall and Wann Langston Jr. |
| Location of First Find | Antlers Formation, Oklahoma, USA |
| First Described | 1950 by J. Willis Stovall and Wann Langston Jr. |
| Holotype | OMNH 10146 and OMNH 10147 |
Acrocanthosaurus Origins: Taxonomy, Timeline, and Discovery
Acrocanthosaurus, a name that resonates with a certain grandeur, is derived from the Greek words ‘akra’, meaning ‘high’, ‘akantha’, meaning ‘thorn’ or ‘spine’, and ‘sauros’, meaning ‘lizard’. This nomenclature is a testament to the dinosaur’s distinctive high-spined vertebrae, a feature that sets it apart from its contemporaries.
Belonging to the Theropod group, it is a member of the Carcharodontosaurid family. Its type species is Acrocanthosaurus atokensis, which serves as a testament to its unique characteristics within the group.
Our journey through time takes us back to the Early Cretaceous period, specifically the Late Aptian to Albian epoch. This was a time when Acrocanthosaurus roamed the Earth, approximately 122.46 to 100.5 million years ago.
The first discovery of its fossils dates back to 1940 in Oklahoma, USA. This significant find was made by American paleontologists J. Willis Stovall and Wann Langston Jr., who also described the dinosaur in 1950, contributing to our understanding of this fascinating creature.
Listen to Pronunciation
Fossil Evidence
The first discovery in 1940 marked a significant milestone in paleontology. The fossils were found in Oklahoma, USA, by J. Willis Stovall and Wann Langston Jr., who also described the dinosaur in 1950. This discovery provided the first glimpse into the existence of this high-spined lizard.

Subsequent finds have further enriched our understanding of Acrocanthosaurus. Fossils attributed to this dinosaur have been found in several states across the present-day United States, including Arkansas, Maryland, Texas, Utah, and Wyoming. These discoveries have painted a broader picture of its geographical range during the Cretaceous period.
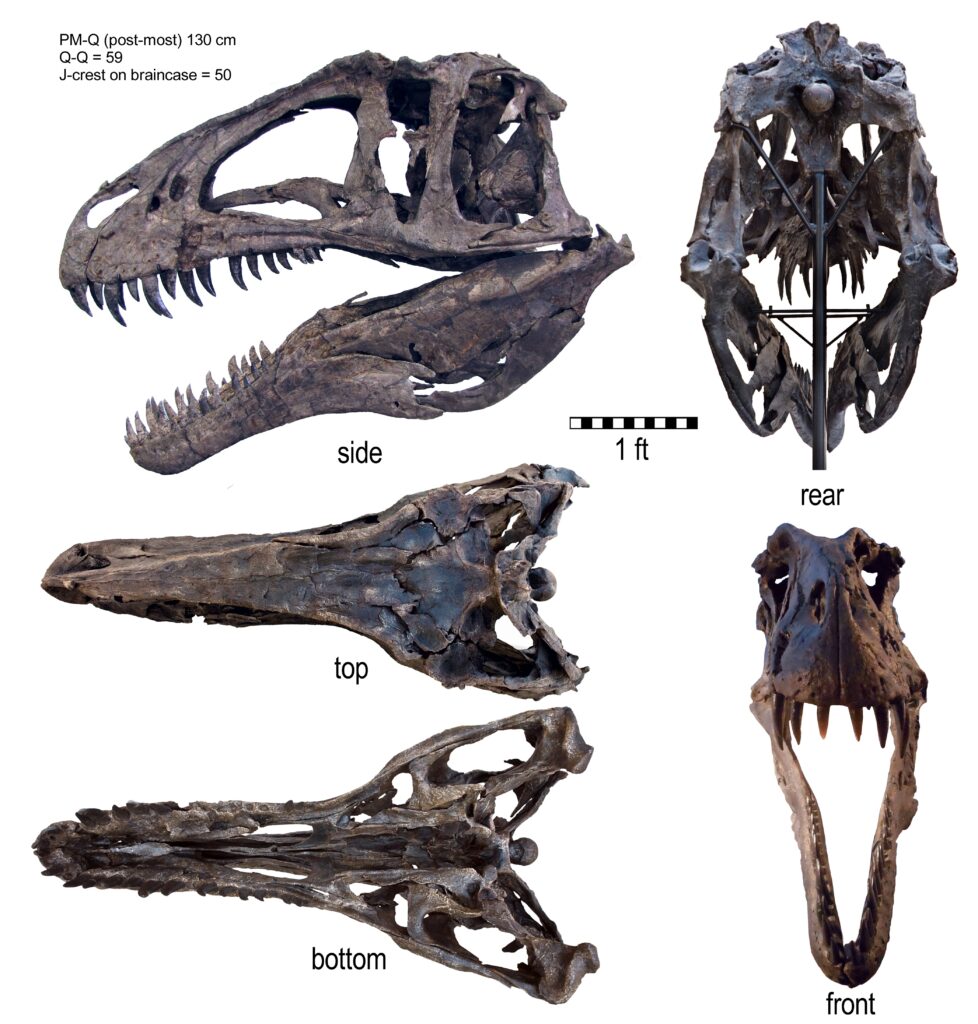
The fossils unearthed have varied in their degree of preservation, with some impressive specimens providing valuable insights into the dinosaur’s physical characteristics–most notable among these is the high-spined vertebrae, a feature that has become synonymous with Acrocanthosaurus and has played a crucial role in its identification.
Acrocanthosaurus Size and Description
The Acrocanthosaurus is a dinosaur that commands attention, not just for its high-spined vertebrae, but also for its overall physical characteristics. Let’s go into an overview of these characteristics to understand what sets it apart from its contemporaries.
Short description of Acrocanthosaurus
The Acrocanthosaurus was a bipedal dinosaur, moving predominantly on its two hind limbs. Its body was designed for a carnivorous lifestyle, with a large head equipped with sharp teeth for hunting prey. The neck was strong and robust in order to support the head while the tail provided balance during movement. The dinosaur’s most distinctive feature, the high-spined vertebrae, ran along its back and contributed to its unique silhouette.
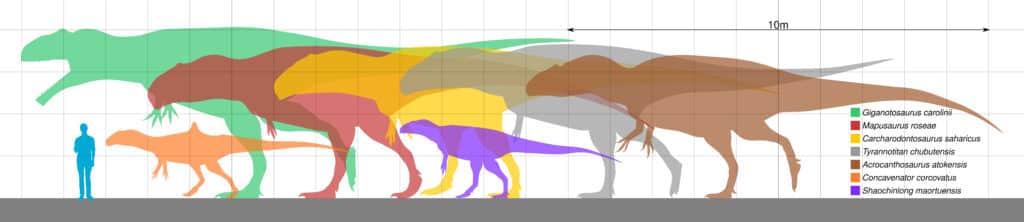
Size and Weight of Type Species
The size and weight of Acrocanthosaurus have been subjects of much discussion among paleontologists. Estimates suggested that Acrocanthosaurus was a large theropod. However, the exact dimensions and weight can vary based on different interpretations of the available fossil evidence.
The Ultimate Dino Quiz
Do you want to test your knowledge of dinosaurs? Then try this Ultimate Dino Quiz! Don’t worry if you get some of the answers wrong, and look at it as an opportunity to refresh and improve your knowledge!
Don’t forget to try our other games as well!
The Acrocanthosaurus in Detail
The Acrocanthosaurus is a dinosaur that stands out, not just for its size, but for its unique features. Most importantly among these is its high-spined vertebrae, from which it gets its name. However, combined with its robust body structure, these vertebrae suggest a dinosaur built for strength and endurance. They also hint at the dinosaur’s adaptability. It is possible that these spines supported a hump or ridge of flesh to store food or fat, helping the dinosaur survive in harsh conditions. This adaptability may have been a key factor in its survival during the Early Cretaceous period.
Above all, specimens of Acrocanthosaurus have provided valuable insights into this dinosaur. These specimens, each unique in their own way, have contributed to our understanding of the dinosaur’s physical characteristics, lifestyle, and behavior.
The Acrocanthosaurus in its Natural Habitat and Environment
The Acrocanthosaurus lived during the Early Cretaceous period, a time when the Earth was undergoing significant changes. The climate was warm and sea levels were rising, creating a landscape of shallow seas and lush vegetation. During the Early Cretaceous, North America was split into two paleocontinents–Laramidia and Appalachia–divided by a seaway. Its fossils have been found on both paleocontinents so far.
As a carnivorous dinosaur, it was at the top of the food chain. Its diet likely consisted of smaller dinosaurs and other terrestrial vertebrates. Its bipedal locomotion suggests a predator capable of chasing down its prey, while its robust body structure indicates a dinosaur capable of taking down larger prey.
The Acrocanthosaurus, with its size and strength, likely played a significant role in shaping the ecosystem around it. For example, as a top predator, it would have had a significant impact on the populations of its prey species and influenced the balance of the ecosystem.
Interesting Points about Acrocanthosaurus
- The name, meaning ‘High-spined lizard’, is a reference to its distinctive high-spined vertebrae.
- It was a top predator during the Early Cretaceous period, indicating its significant role in the ecosystem.
- Fossils have been found across several states in the United States, suggesting a wide geographical range across both North American paleocontinents.
- Notable specimens have provided valuable insights into this dinosaur’s physical characteristics and lifestyle.
Contemporary Dinosaurs
During the vast expanse of prehistoric time, the Acrocanthosaurus, a creature of formidable presence, shared its world with a captivating ensemble of contemporaries. Among these were the Deinonychus, Tenontosaurus, and Sauroposeidon, each playing their part in the intricate ballet of survival and competition that defined their era.
The Deinonychus, smaller yet agile, might have been a frequent sight in the Acrocanthosaurus’s environment. Their potential interactions paint a vivid picture of the predator-prey dynamics of the time. The nimble Deinonychus, with its sharp claws and swift movements, could have been both a competitor and a potential prey for the larger Acrocanthosaurus. On the other hand, the Tenontosaurus, an herbivore, offers a contrast to the carnivorous Acrocanthosaurus. Their coexistence suggests a delicate balance, with the Tenontosaurus possibly serving as a food source for the Acrocanthosaurus while also competing for resources like water and space.
The Sauroposeidon, towering above the landscape, was a contemporary Laramidian dinosaur. It’s sheer size and herbivorous diet would have set it apart from the Acrocanthosaurus. Therefore, their shared environment implies a complex relationship. The Acrocanthosaurus, despite its own impressive size, would have been dwarfed by the Sauroposeidon. This size difference might have allowed for a peaceful coexistence rather than sparking conflict, with each species occupying its own niche in the ecosystem. But, through this exploration, we gain a deeper understanding of the Acrocanthosaurus’s life, its interactions, and the world it inhabited.
Featured Image Credit: Mariolanzas, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Sources
Please note that the information in this article is based on various sources, drawing on scientific research, fossil evidence, and expert analysis. We aim to provide a comprehensive and accurate overview of the dinosaurs, but please be aware that our understanding of dinosaurs and their world is constantly evolving as new discoveries are made.
Article last fact checked: Joey Arboleda, 06-09-2023

