Imagine, if you will, a creature of such immense size that it dwarfs modern elephants, a creature that roamed our planet during a time when it was a vastly different place. This creature is none other than the Apatosaurus, a dinosaur that has long captivated the minds of both scientists and dinosaur enthusiasts alike. This colossal herbivore, hailing from the Late Jurassic period, serves as a testament to the diverse and vibrant life that once inhabited our world.
Key Facts
| Keyword | Fact |
|---|---|
| Apatosaurus pronunciation | uh-paa-tuh-saw-ruhs |
| Meaning of name | Deceptive lizard |
| Group | Sauropod |
| Type Species | Apatosaurus ajax |
| Diet | Herbivore |
| When it Lived | 155.7 to 145.0 MYA |
| Period | Late Jurassic |
| Epoch | Late Kimmeridgian to Early/Lower Tithonian |
| Length | 75.0 to 90.0 ft |
| Height | 18.0 to 21.3 ft |
| Weight | 22.4 to 40 tons |
| Mobility | Moved on all four |
| First Discovery | 1877 by Arthur Lakes and Henry Beckwith |
| Location of first find | Colorado, USA |
| First Described by | 1877 by Othniel Charles Marsh |
| Holotype | CM 3018 |
Apatosaurus Origins: Taxonomy, Timeline, and Discovery
In addition, the name “Apatosaurus” carries with it a sense of intrigue. Translating to “deceptive lizard,” this dinosaur’s name is derived from the Greek words “apatē,” meaning deception, and “sauros,” meaning lizard. This name was given due to the confusion surrounding its fossilized remains, which were initially thought to belong to a different kind of reptile.
Belonging to the group Sauropodomorpha, specifically the family Diplodocidae, the Apatosaurus is known for its long neck and tail, features characteristic of this group of dinosaurs. Within this genus, the type species is Apatosaurus ajax and a notable subspecies is Apatosaurus louisae.
The timeline of the Apatosaurus is set in the Late Jurassic period, specifically from the Late Kimmeridgian to the Early Tithonian epochs. This places the age range of the Apatosaurus between 155.7 to 145 million years ago, a time when the earth was teeming with a variety of life forms.
The first discovery of the Apatosaurus was made in 1877 in Colorado, USA, by Arthur Lakes and Henry Beckwith. This discovery was later described by the American paleontologist Othniel Charles Marsh, who initially believed the bones belonged to a different dinosaur, leading to the name “deceptive lizard.”
Listen to Pronunciation
Fossil Evidence
The first fossil evidence of the Apatosaurus was discovered in the Morrison Formation. This discovery, made in 1877, was a significant milestone in paleontology. The Morrison Formation, located in the western United States, has been a treasure trove of dinosaur fossils, offering a glimpse into the diverse life forms that once roamed this region.
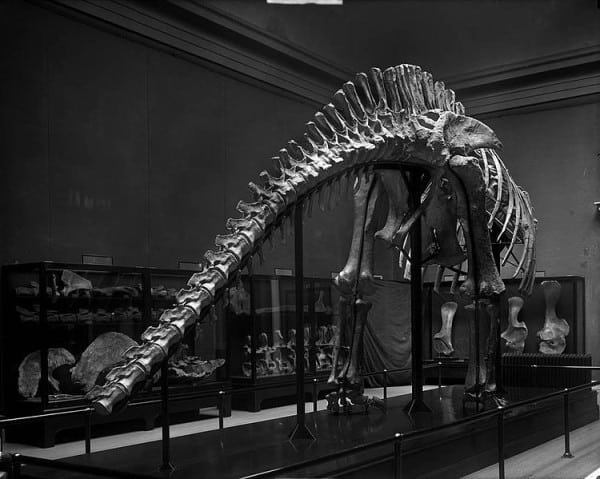

As such, the fossils of the Apatosaurus discovered here have provided a wealth of information about this fascinating creature and others like it. Found fossils include vertebrae, limb bones, and even impressions of the dinosaur’s skin. Each fossil discovery has added a new piece to the puzzle, helping us understand the physical characteristics and lifestyle of the Apatosaurus.
Apatosaurus Size and Description
The Apatosaurus was a truly colossal creature. Its long neck and tail, coupled with its massive body, made it one of the largest land animals to have ever existed.
Short description of Apatosaurus
Therefore, the Apatosaurus was characterized by its long neck and tail, which it used for balance and possibly defense. Its body was massive, supported by sturdy legs, and it moved on all fours. Also, the dinosaur’s skin was likely rough, similar to that of modern reptiles. Its long neck allowed it to reach vegetation that other dinosaurs couldn’t while its whip-like tail could have been used for defense. The Apatosaurus was a giant among dinosaurs, a testament to the incredible diversity of life during the Jurassic period.
Size and Weight of Type Species
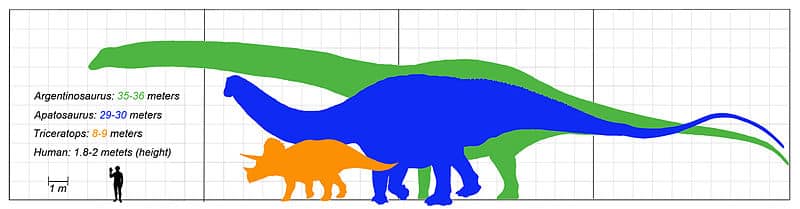
It was a giant among dinosaurs. Some estimated them to have been around 75 to 90 feet long and weighed as much as 22.4 to 40 tons. However, these estimates vary, with some suggesting that the dinosaur could have been even larger. Despite its size, the Apatosaurus was likely a slow-moving creature, its massive body requiring a lot of energy to move. Regardless of its exact size, there’s no doubt that the Apatosaurus was one of the largest creatures to have ever walked the earth.
Apatosaurus Illustration Sketch
The Dinosaur in Detail
Some of the features that set the Apatosaurus apart from other dinosaurs include its long neck allowed it to reach vegetation that other dinosaurs couldn’t and its whip-like tail that could have been used for defense. Furthermore, this dinosaur’s massive size would have made it a formidable presence in its environment, and its unique features reflect its adaptability and survival instincts.
The distinctive neck, which could reach lengths of up to 30 feet, would have given it a significant advantage when it came to finding food. The tail, which could reach lengths of up to 50 feet, was likely used for defense against predators. The tail could have been swung like a whip, creating a sonic boom that would have been enough to deter any potential predators.
It also had a unique skeletal structure. Its vertebrae were lighter than those of other dinosaurs, thanks to a system of air sacs. These air sacs, similar to those found in modern birds, would have lightened the dinosaur’s body, making it easier for it to support its massive size.
The Apatosaurus in its Natural Habitat and Environment
The Apatosaurus lived in North America during the Late Jurassic period, a time when the earth was a very different place than it is today. The environment during this time was semi-arid, with forests, rivers, and floodplains.
As an herbivorous dinosaur, the Apatosaurus would have fed on the abundant vegetation in its environment. Its long neck would have allowed it to reach plant material that other dinosaurs couldn’t, giving it a significant advantage when it came to finding food. The Apatosaurus likely moved in herds, traveling from one feeding ground to another.
The Apatosaurus’s massive size would have made it an unmistakable presence in its environment. It’s likely that the dinosaur had few predators, thanks to its size and its whip-like tail, which could have been used for defense. Despite its size, the Apatosaurus was likely a slow-moving creature due to the large amount of energy required to move a body of that size.
Interesting Points about Apatosaurus
- It had a unique skeletal structure, with lighter vertebrae than other dinosaurs. This was due to a system of air sacs, similar to those found in modern birds, which lightened the dinosaur’s body.
- Its long neck allowed it to reach vegetation that other dinosaurs couldn’t, giving it a significant advantage when it came to finding food.
- Despite its massive size, it was likely a slow-moving creature. Its massive body would have required a lot of energy to move, making it unlikely that the dinosaur was a fast runner.
Contemporary Dinosaurs
The Apatosaurus, a creature of monumental stature, shared its Jurassic world with a fascinating ensemble of North American dinosaurs. These fellow dinosaurs, each unique in their own right, played a part in the intricate dance of existence. Their lives intertwined in a complex web of survival and competition.
Among these contemporaries was the Allosaurus, a terrifying predator. While the Apatosaurus was a peaceful herbivore, the Allosaurus was its stark contrast, a carnivore with a taste for flesh. Yet, despite their differences, these two creatures coexisted, a testament to the delicate balance of nature.
The Camarasaurus, another contemporary, shared a similar diet with the Apatosaurus. Both were herbivores, feeding on the lush vegetation of their shared habitat. Yet, their coexistence was not one of rivalry but of harmony. The Camarasaurus, being smaller, fed on lower vegetation, while the Apatosaurus reached for the treetops. This division of resources allowed them to live side by side without direct competition.
Lastly, the Diplodocus, a fellow long-necked dinosaur, shared the landscape with the Apatosaurus. Their similar body structures might suggest a rivalry, but their differing feeding habits ensured a peaceful coexistence. The Diplodocus, despite its size, fed on ground-level vegetation, leaving the high branches to the Apatosaurus. This intricate balance of resource utilization is a testament to the complex dynamics of prehistoric life. Together, these dinosaurs created a diverse and vibrant ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions
The name translates to “deceptive lizard.” It was given because of its unique skeletal structure. Initially it was thought to be similar to that of other dinosaurs.
It was a giant among dinosaurs. It is estimated to have been around 75 up to 90 feet long and weighed as much as 40 tons. However, these estimates vary, with some suggesting that the dinosaur could have been even larger.
It lived during the Late Jurassic period. This was a time when the earth was a very different place than it is today. The large landmasses were semi-arid environments with distinct wet and dry seasons.
Fossils have been found in the Morrison Formation. It spans several US states, including Wyoming, Colorado, and Montana. The Morrison Formation is a rich source of dinosaur fossils. It offers a glimpse into the diverse life forms that once roamed this region.
It had several unique features that set it apart from other dinosaurs. These include its long neck, and its whip-like tail. The dinosaur also had a unique skeletal structure. Made up of lighter vertebrae than other dinosaurs, thanks to a system of air sacs.
Sources
Article last fact checked:Joey Arboleda, 06-10-2023
