Step back in time to a world where the ancient Miragaia roamed–a realm of giants and survival. In this prehistoric dance, Miragaia, with its distinctive long neck, navigated a landscape filled with both allies and adversaries. Imagine this remarkable dinosaur amidst the towering ferns as a part of a dynamic ecosystem where every creature played a vital role.
In this world, Miragaia encountered the likes of Allosaurus and Stegosaurus, each with their unique traits and survival strategies. Their interactions, whether competitive or cautious, painted a vivid picture of life millions of years ago. Join us as we explore the fascinating dynamics between this dinosaur and its contemporaries by delving into a time when these magnificent creatures ruled the Earth.
Miragaia Key Facts
| Keyword | Fact |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | MERE-ah-gai-ah |
| Meaning of name | Church and geological formation in Portugal |
| Group | Stegosauria |
| Type Species | Miragaia longicollum |
| Other Species | Miragaia longispinus |
| Diet | Herbivore |
| When it Lived | 155.7 to 150.8 MYA |
| Period | Late Jurassic |
| Epoch | Late/Upper Kimmeridgian |
| Length | 20.0 to 21.0 feet |
| Height | Approximately 6.0 feet |
| Weight | 2.2 tons |
| Mobility | Moved on all four |
| First Discovery | 1999 and 2000, by construction workers |
| Described by | 2009 by Octávio Mateus and others |
| Holotype | ML 433 |
| Location of first find | Villages of Miragaia and Sobral, Portugal |
| Also Found in | Wyoming (USA) |
Miragaia Origins, Taxonomy and Timeline
This dinosaur’s name is a nod to its place of discovery. The geologic formation in Portugal from which it was excavated is also named Miragaia, after a local church. Later finds suggest a much broader range that includes western North America.
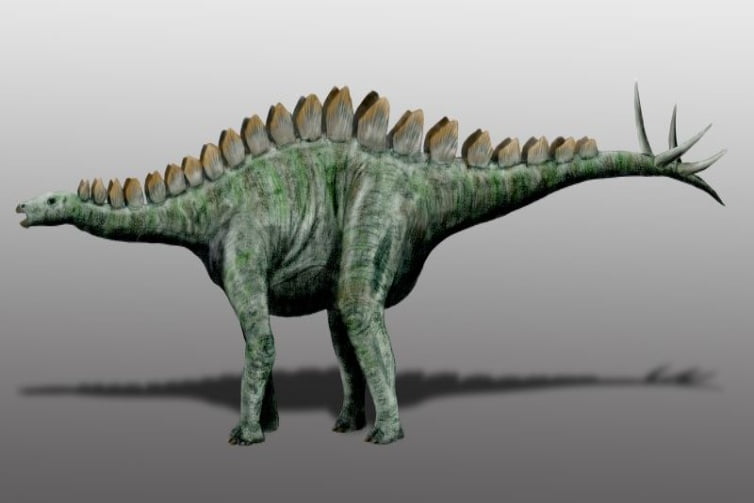

As a member of the Stegosauria group and the Stegosaurid family, Miragaia represents a lineage known for their distinctive plates and spikes. The type species Miragaia longicollum however is known for something else. Interestingly, it has the longest neck among the stegosauria dinosaurs. Individual evolution and adaptation is at play when we try to explain this interesting characteristic. This genus includes a second species, Miragaia longispinus.
This story is set in the Late Jurassic Period, specifically in the Late Kimmeridgian Epoch. This time frame, spanning from 155.7 to 150.8 million years ago, was a period of significant ecological and geological changes. It was a world where Miragaia shared the landscape with a myriad of other species, each playing a role in the complex ecosystem of the time.
Discovery & Fossil Evidence

The story of discovery begins in the late 1990s, in the villages of Miragaia and Sobral in Portugal. It’s a tale not of seasoned paleontologists, but of alert construction workers who stumbled upon something extraordinary. Their find would later be classified as the holotype ML 433. It marked the beginning of Miragaia’s journey from a buried relic to a subject of scientific study.
The subsequent description of Miragaia in 2009 by paleontologists Octávio Mateus, Susannah Maidment, and Nicolai Christiansen was not just about adding another name to the list of known dinosaurs. It was about understanding the nuances of its anatomy and the peculiarities that set it apart from its cousins in the Stegosaurid family. The fossils, while not complete, provided enough evidence to paint a picture of a creature that was as intriguing as it was unique.
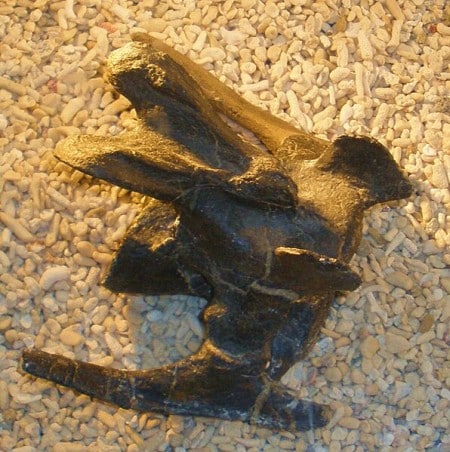

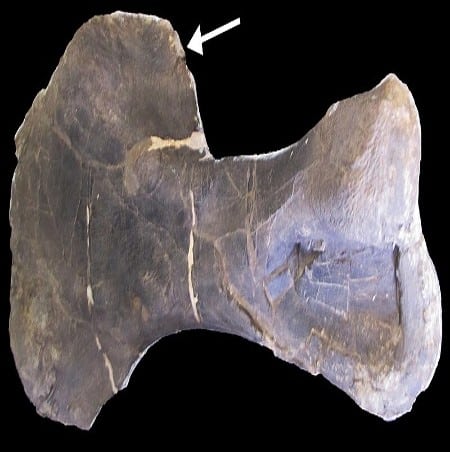
Miragaia’s fossil record, though limited, speaks volumes. The degree of preservation varies, but each fragment and bone adds to the puzzle. From these remnants, scientists have been able to glean insights into its physical characteristics, its place in the ecosystem, and even its behavior.
Miragaia Size and Description
This relative of Stegosaurs shows a unique place near the end of their evolution. Its generally robust build and platy back may resemble the rest of its family, but its neck is its most defining feature that sets it apart. Its long and lightweight body paired with its intimidating tail spikes paints the picture of a gentle herbivore capable of defending itself.
Size and Weight of Type Species
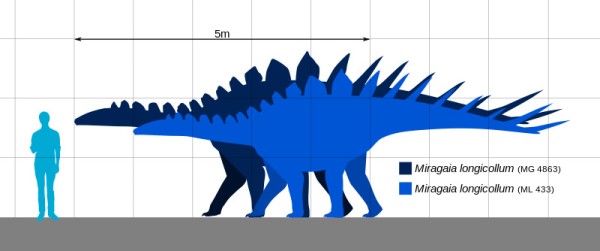
Miragaia, a unique member of the Stegosaur family, was notable for its length and relatively light build. This dinosaur stretched to an impressive 20.0 to 21.0 feet in length, yet its body mass was around 2.2 tons. This makes it lighter compared to other Stegosaurs. The age of the holotype specimen was determined through histology as approximately 21 years, providing insights into the lifespan and growth patterns of this species.
The Dinosaur in Detail
This dinosaur had several distinguishing traits that set it apart from its peers. The praemaxillae–a bone at the very midline of its snout–met in a small, sharp point nestled within a larger notch at the snout tip. This feature, along with the protruding front lower side edge of the praemaxilla, contributed to its unique facial structure. Miragaia also had at least seventeen neck vertebrae, a notable deviation from other Stegosaurians. This is more than most sauropods! The neural spines on top of the middle neck vertebrae were uniquely shaped, featuring a notch at their lower front edge and a process directed forward. On its neck, Miragaia displayed two rows of triangular bony plates.
This unique adaptation might have allowed Miragaia to browse at levels unexploited by other herbivores. It could have also been a result of sexual selection, a theory proposed by researchers. This long neck not only redefines our understanding of Miragaia’s feeding habits but also highlights the diverse evolutionary pathways within Stegosaurians.
Interesting Points about Miragaia
- Its elongated neck was unusual for a Stegosaurid and suggests a unique feeding strategy or a distinctive display feature.
- This discovery in Portugal, coupled with later finds in Wyoming, USA, indicates a wider geographical distribution than initially thought for Stegosaurids.
- Despite the incomplete nature of its fossil record, it has contributed significantly to our understanding of Stegosaurid diversity and evolution.
- The combination of plates and spikes on its back is typical of Stegosaurids and might have had multiple functions, including defense, thermoregulation, and attracting mates.
- Its discovery by construction workers highlights the role of chance and the contributions of non-scientists in paleontological discoveries.
Miragaia in its Natural Habitat
Imagine a world where this herbivorous dinosaur roamed – a landscape marked by lush vegetation, diverse ecosystems, and dynamic geological formations. This Late Jurassic environment, characterized by a warm climate and abundant plant life, provided the perfect backdrop for Miragaia’s lifestyle. The variety of flora not only served as its primary food source but also shaped the interactions within its ecosystem.
As a large herbivore, this dinosaur played a crucial role in its habitat. Its diet likely consisted of a range of plants, from ferns to conifers, which it accessed with its elongated neck. This feeding strategy not only influenced its physical development but also its interactions with other species. As a four-legged dinosaur, its locomotion was adapted to navigating this verdant world in search of the best grazing spots.
The social behavior of Miragaia, whether it was a solitary wanderer or a herd animal, remains a subject of speculation. However, its physical attributes such as its defensive spikes suggest a creature well-equipped to defend itself, possibly indicating interactions with predators. Its role in the ecosystem, from shaping the vegetation through grazing to possibly influencing the behavior of other species, underscores its importance in the Late Jurassic world.
Contemporary Dinosaurs
Imagine this dinosaur’s elongated neck and striking body meandering through ferns and cycads, a gentle giant amidst a world of titanic beasts. It was smaller than fearsome Allosaurus, a predator whose presence in the forest could turn a peaceful graze into a frantic escape. Yet, in this ancient drama, Miragaia wasn’t just a bystander. Its size was modest compared to Allosaurus but it was formidable enough to make it more than just easy prey.
Stegosaurus, a fellow herbivore, ambled across this landscape as well. While they didn’t directly confront each other, the way they shared – or monopolized – resources shaped their daily lives. Not far off, Dacentrurus, another contemporary Stegosaurian, made its presence known. Larger than Miragaia, it boasted formidable spikes in a display that could deter even the most daring of predators. This size difference meant that Miragaia had to be more strategic in its movements and choices, always aware of the larger herbivores and the space they commanded.
Then there was Ceratosaurus, a predator smaller than Allosaurus but no less daunting. Its interactions with Miragaia were likely a mix of cautious avoidance and, on unfortunate days, desperate flight. Though not the largest or the fiercest, Miragaia was a crucial part of this prehistoric tapestry. Its life was intertwined with these contemporaries in a delicate balance of coexistence and competition throughout the rich and complex ecosystem of its time.
Frequently Asked Questions
It lived during the Late Jurassic Period, specifically in the Late Kimmeridgian Epoch.
It was an herbivore that used its longer neck to feed on the abundant plant life of its time.
It was first discovered by construction workers in Portugal in the late 1990s.
Its elongated neck, unusual for a Stegosaurid, sets it apart and suggests unique feeding or display behaviors.
The fossils were initially found in Portugal, with later finds of another species in Wyoming, USA.
As an herbivore, it played a key role in shaping the vegetation and interacting with other species in its Late Jurassic habitat.
Sources
The information in this article is based on various sources, drawing on scientific research, fossil evidence, and expert analysis. The aim is to provide a comprehensive and accurate overview of Miragaia. However, please be aware that our understanding of dinosaurs and their world is constantly evolving as new discoveries are made.
This article was last fact-checked: Joey Arboleda, 12-09-2023
Featured Image Credit: Nobu Tamura, CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
