Europasaurus, a small-sized sauropod, was a stark contrast to its typically gigantic relatives. At only 20 feet and around 1 US ton, it paints a fascinating picture of adaptability and survival in the Late Jurassic period. Its discovery in the late 20th century in the heart of Europe added a new dimension to our understanding of sauropod diversity and evolution.
Europasaurus Key Facts
| Keyword | Fact |
|---|---|
| Europasaurus pronunciation | YOO-roh-puh-SAWR-us |
| Meaning of name | “Europe’s lizard” |
| Group | Sauropoda |
| Type Species | Europasaurus holgeri |
| Diet | Herbivore |
| When it Lived | 155.7 – 150.8 MYA |
| Period | Late Jurassic |
| Epoch | Late/Upper Kimmeridgian |
| Length | 20.0 ft |
| Height | 10 ft |
| Weight | 0.90 US tons |
| Mobility | Moved on all four |
| First Discovery | 1998 by Holger Lüdtke |
| Location of first find | Süntel Formation, Germany |
| First Described by | 2006 by Martin Sander, Octávio Mateus, Thomas Laven, Nils Knötschke |
| Holotype | DFMMh/FV 291 |
Europasaurus Origins, Taxonomy and Timeline
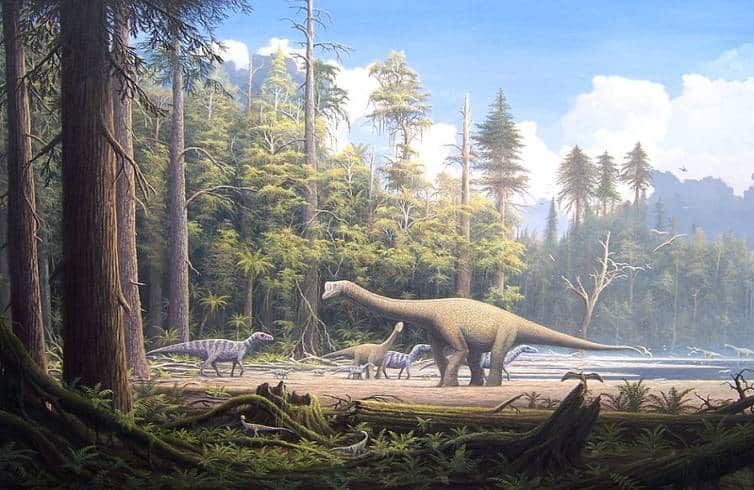

The name Europasaurus, meaning “Europe’s lizard”, is a mix of its location of discovery and its unique place in the dinosaur kingdom. This small-sized sauropod, a member of the group Sauropoda, stands out among its typically larger relatives. Its name, etymology, and classification all contribute to its fascinating identity.
Belonging to the family Camarasauromorpha and the type species E. holgeri, Europasaurus is a unique specimen in the world of dinosaurs. Its taxonomic classification places it in the sauropoda group. However, its smaller size sets it apart and adds a layer of intrigue to its existence.
This dinosaur lived during the Late Jurassic period, specifically during the Upper Kimmeridgian epoch, . This was a time when the Earth was dominated by dinosaurs and the Europasaurus was a unique player in this prehistoric world.
Listen to Pronunciation
To get a better sense of how to pronounce Europasaurus, you can listen to the pronunciation.
Discovery & Fossil Evidence
This story began with an unexpected discovery in the late 20th century. In 1998, Holger Lüdtke, a German private fossil collector, stumbled upon a set of intriguing fossils in the Süntel Formation in Germany. This region was known for its rich fossil deposits and had now revealed a new player in the prehistoric world– Europasaurus.
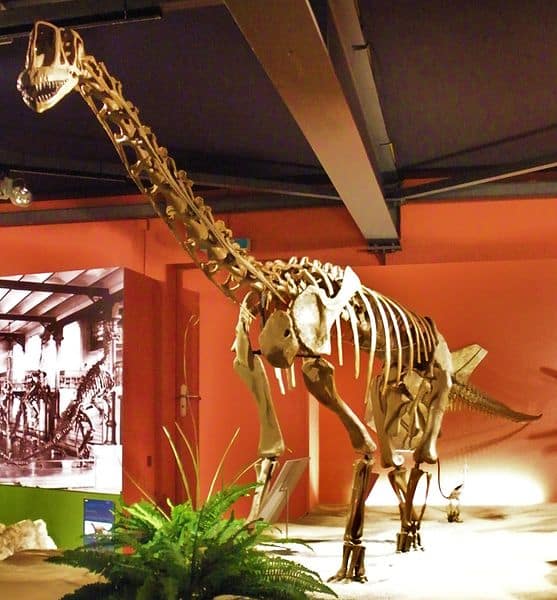

Since the initial discovery, the Süntel Formation has continued to yield more of these fossils. These subsequent finds have provided a more comprehensive picture of this unique dinosaur. The fossils found include partial skeletons and individual bones, such as vertebrae and limb bones. Each new find adds another piece to the puzzle that helps scientists to piece together the physical characteristics and lifestyle of the Europasaurus.
The fossils vary in their degree of preservation. Some are remarkably well-preserved and provide detailed information about the dinosaur’s physical characteristics. Notable specimens include a nearly complete skull and a series of articulated vertebrae. These fossils have been instrumental in our understanding of the dinosaur by revealing its small size, robust skeletal structure, and unique dental features. As more fossils are discovered and studied, we continue to learn more about this fascinating dinosaur and its place in the prehistoric world.
Europasaurus Size and Description
Europasaurus was a small-sized sauropod despite belonging to a group typically known for their large size. This dinosaur had a long neck and tail, a small head, and a robust body. Its limbs were strong and sturdy, designed to support its body weight. It moved on all four legs–a common characteristic among sauropods.
Its skin, like some other dinosaurs, was likely covered in scales. While the exact color and pattern of its skin are unknown, it’s plausible that it had coloration that helped it blend into its environment. The dinosaur’s speed is also unknown but considering its size and body structure it was likely not a fast mover.
Size and Weight of Type Species
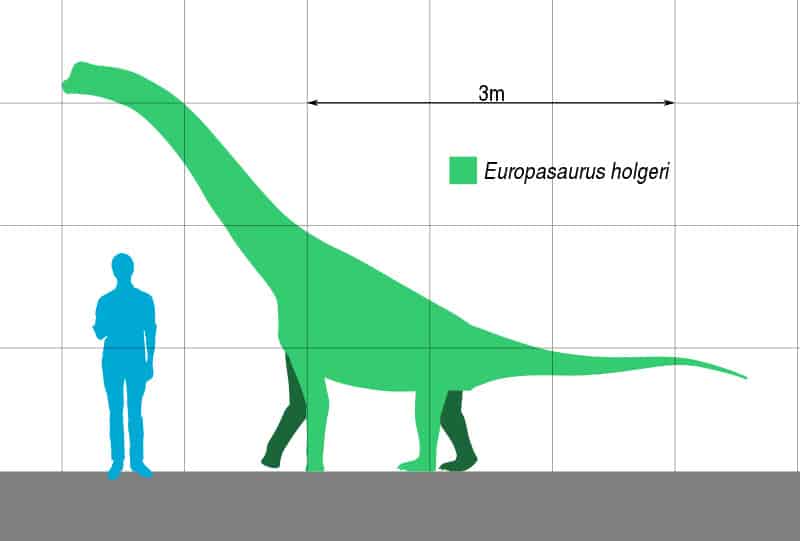
The size is one of its most intriguing aspects. Unlike other sauropods, which were known for their massive size, this species was relatively small. While the exact size and weight are not known, it’s estimated that this dinosaur was significantly smaller than its sauropod relatives.
Based on the fossils found, it’s believed that it was about 20 feet long. This is quite small compared to other sauropods that could reach lengths of over 100 feet. The dinosaur’s weight is estimated to have been around 1 US ton.
These size estimates are based on the fossils found thus far and may change as more fossils are discovered and studied. Despite the uncertainties, one thing is clear, Europasaurus was a unique dinosaur that challenged our perceptions of what a sauropod could be.
The Dinosaur in Detail
One of the most distinctive features of this dinosaur is its size. Unlike its sauropod relatives which are known for their colossal stature, the Europasaurus was a dwarf sauropod that reached a length of approximately 20 ft. This size difference is believed to be a result of insular dwarfism–a form of adaptive evolution where the size of a species is significantly reduced over time due to the limited resources available in an isolated environment.
Another notable feature of Europasaurus is its robust skeletal structure. Despite its smaller size, this dinosaur had a strong and sturdy skeleton. In particular, its vertebrae were compact and solid in order to provide the necessary support for its long neck and tail. This robust skeletal structure combined with its small size would have allowed this herbivore to move efficiently and navigate its environment with ease.
It also had a unique dental structure. Unlike the spoon-shaped teeth that were typical for other sauropods, this dinosaur had pencil-shaped teeth. These teeth were well-suited for its herbivorous diet and allowed it to efficiently strip leaves off branches and consume a variety of plant matter.
Europasaurus in its Natural Habitat
This herbivorous dinosaur thrived in a world vastly different from ours. During the Late Jurassic period, the European environment was characterized by a warm and humid climate with lush vegetation covering the landscape. This environment provided the perfect backdrop for this herbivore to thrive.
The diet of Europasaurus consisted primarily of plant matter. With its long neck and small, pencil-shaped teeth, it was well-equipped to strip leaves off branches and consume a variety of vegetation. The abundance of plant life in its environment ensured a steady food supply for this dinosaur.
It was a quadruped that moved on all four legs. This mode of locomotion and its robust skeletal structure allowed it to navigate its environment with ease. While the exact social behavior of this dinosaur is unknown, it’s plausible that it lived in herds like many other sauropods. Living in groups could have offered protection from predators and increased access to food resources.
Interesting Points about Europasaurus
- It is one of the smallest known sauropods that reached a length of approximately 20 ft.
- The size difference between this species and other sauropods is believed to be a result of insular dwarfism.
- It had a robust skeletal structure with compact and solid vertebrae.
- Unlike other sauropods, it had pencil-shaped teeth that were well-suited for its herbivorous diet.
- It was first discovered in 1998 in the Süntel Formation in Germany, a location known for its rich fossil deposits.
Contemporary Dinosaurs
Europasaurus existed along with a diverse array of contemporary European dinosaurs. Among these were Juravenator, Allosaurus, Brachiosaurus, and Camptosaurus–each contributing to the intricate dynamics of this ancient ecosystem.
Europasaurus, despite its smaller stature compared to some of its contemporaries, held its own in this vibrant prehistoric world. The nimble Juravenator was a fellow dino of this era and a stark contrast to Europasaurus. Its lithe form and predatory nature presented a fascinating counterpoint to our main dinosaur’s more robust and herbivorous lifestyle. Yet, these two species coexisted, each fulfilling their own niche in the ecosystem.
Camptosaurus, another herbivore, shared a similar size and lifestyle with the Europasaurus. Their coexistence offers a glimpse into the possible camaraderie or competition for resources among herbivorous dinosaurs. Despite their shared dietary preferences, the Camptosaurus and Europasaurus each had their unique adaptations that allowed them to coexist and thrive.
Allosaurus and Brachiosaurus, both considerably larger than Europasaurus, shed some light on the scale of life during this period. Allosaurus was a formidable predator that might have posed a significant threat to Europasaurus. On the other hand, the towering Brachiosaurus was a gentle giant subsisting on plant life that would have been a sight to behold for the smaller Europasaurus. These interactions, whether adversarial or indifferent, were part of the complex web of existence that defined the life of Europasaurus. This intricate dance of survival, competition, and coexistence paints a vivid picture of the life of our dinosaur.
List of All Dinosaurs
We have created a list of all dinosaurs we have covered here, sorted across the seven main groups of dinosaurs. We also include information about their type of diet, (omnivore, herbivore or carnivore) and the time they lived.
Frequently Asked Questions
It was one of the smallest known sauropods, reaching a length of approximately 20 ft.
The Europasaurus was an herbivore that fed primarily on plant matter. Its pencil-shaped teeth were perfect for stripping leaves.
This dinosaur lived during the Late Jurassic period, specifically between 155 and 150 million years ago.
The first fossils were discovered in the Süntel Formation in Germany.
It is unique due to its small size compared to other sauropods, its robust skeletal structure, and its pencil-shaped teeth.
It was first discovered by a private fossil collector, Holger Lüdtke, in 1998. The discovery was later described by Martin Sander, Octávio Mateus, Thomas Laven, Nils Knötschke in 2006.
Sources
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/7022223_Bone_histology_indicates_insular_dwarfism_in_a_new_Late_Jurassic_sauropod_dinosaur
- https://paleobiodb.org/classic/basicTaxonInfo?taxon_no=81696
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261175591_Cranial_anatomy_of_the_Late_Jurassic_dwarf_sauropod_Europasaurus_holgeri_Dinosauria_Camarasauromorpha_ontogenetic_changes_and_size_dimorphism
- https://elifesciences.org/articles/82190
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2889090/
This article was last fact checked: Joey Arboleda, 06-08-2023
Featured Image Credit: Gerhard Boeggemann, CC BY-SA 2.5, via Wikimedia Commons
