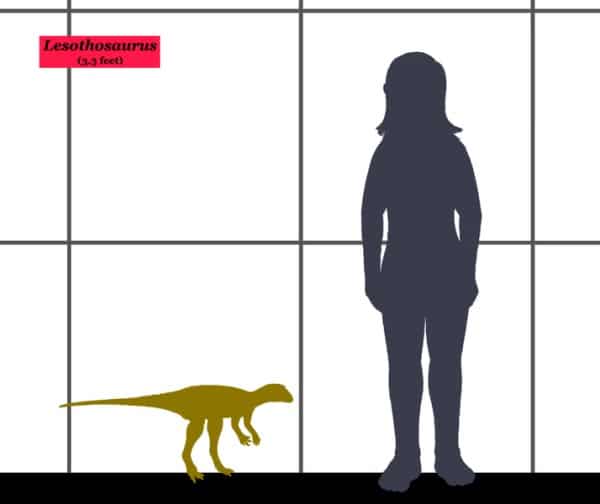
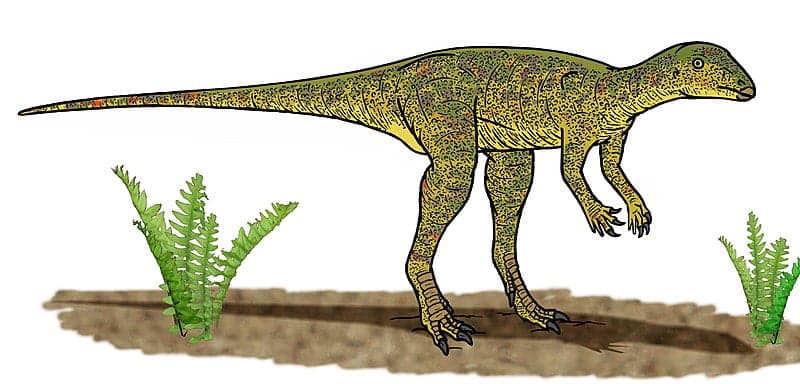
Delving into the prehistoric world, Lesothosaurus stands out as a fascinating subject of study. This small, bipedal dinosaur, whose name translates to “Lizard from Lesotho,” offers a unique glimpse into the early Jurassic Period. Its discovery in the rugged terrains of Southern Africa has provided paleontologists with invaluable insights into the evolutionary journey of dinosaurs. As we explore the life and times of this ancient creature, we invite readers to journey back over 200 million years, to a world vastly different from our own, yet instrumental in shaping the course of natural history.
Lesothosaurus, despite its diminutive size, plays a significant role in our understanding of dinosaur evolution. Its well-preserved fossils, unearthed from the Red Beds of the Elliot Formation, have revealed a creature adapted to a herbivorous lifestyle, navigating a landscape that was undergoing profound ecological shifts. This exploration not only enriches our knowledge of the Jurassic Era but also ignites curiosity about the intricate web of life that once thrived on our planet.
Lesothosaurus Key Facts
| Keyword | Fact |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | Le-SO-toe-sore-us |
| Meaning of name | Lizard from Lesotho |
| Group | Ornithopoda |
| Type Species | Lesothosaurus diagnosticus (syn. Stormbergia dangershoeki) |
| Diet | Herbivore |
| When it Lived | 204 to 192 MYA |
| Period | Late Triassic to Early Jurassic |
| Epoch | Rhaetian to Sinemurian |
| Length | 3.3 to 6.6 feet |
| Height | Approximately 2.0 feet |
| Weight | Approximately 22.0 pounds |
| Mobility | Moved on two legs |
| First Discovery | 1959 by Jean Fabre |
| Described by | 1978 by Peter Malcolm Galton |
| Holotype | NHMUK PV RU B17 & NHMUK PV RU B23 |
| Location of first find | Upper Elliot Formation (Massospondylus Assemblage Zone), Lesotho |
Lesothosaurus Origins, Taxonomy and Timeline
Lesothosaurus, or “Lizard from Lesotho,” owes its name to the country where its remains were first discovered. This nomenclature, combining “Lesotho” with the Greek “sauros” meaning lizard or reptile, succinctly captures the essence of this dinosaur’s origin. Its etymology honors the small Southern African kingdom of Lesotho, a country made of mountains and rightfully nicknamed the Kingdom in the sky. Inhabitants are named Basotho people, and speak Sesotho.

Belonging to the Ornithopoda, this dino is classified within the Ornithischia, with Lesothosaurus diagnosticus serving as its type species. This classification places it firmly within a lineage known for their herbivorous diets and bipedal locomotion, characteristics that distinguish ornithopods from their contemporaries.
Lesothosaurus is found in the upper Elliot Formation of the Massospondylus Assemblage Zone of the Karoo Stormberg Group. Recent datation suggests a timeline between 204 and 192 million years (this is an estimation as no precise dates have been established, especially for the lower boundary of the upper Elliot Formation), see Smith et al., 2020 and Viglietti et al, 2020.
Discovery & Fossil Evidence
The tale of Lesothosaurus’s discovery begins in 1959, when Jean Fabre unearthed the first fossils in the Elliot Formation in Lesotho, Southern Africa. This initial find laid the groundwork for further exploration, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of this dinosaur’s physical characteristics and lifestyle.
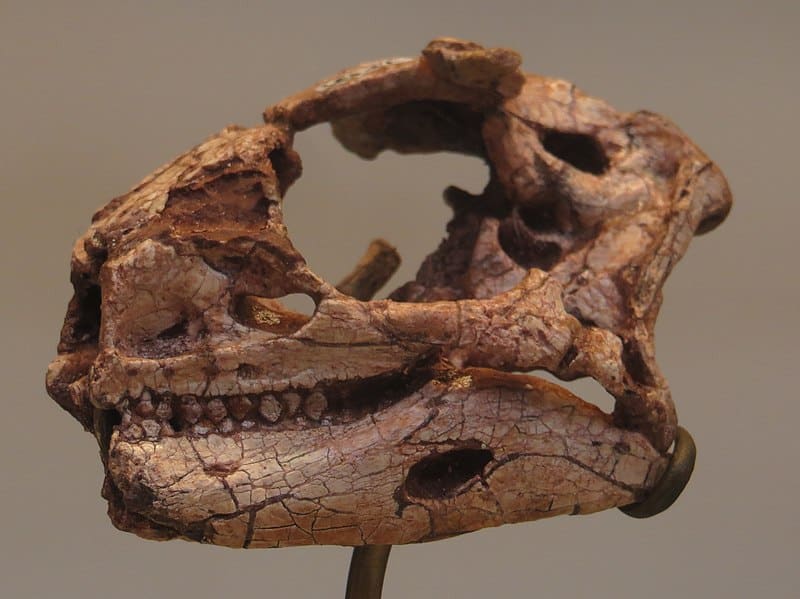

Subsequent excavations have yielded additional fossils, though Lesothosaurus is not known for a vast number of finds. The fossils discovered include a variety of skeletal parts, providing a detailed picture of its anatomy. Notably, the holotypes, NHMUK PV RU B17 & NHMUK PV RU B23, have been instrumental in defining the species, offering a glimpse into its size, shape, and mobility.
These fossils, remarkably well-preserved, have allowed scientists to reconstruct Lesothosaurus’s physical appearance with a fair degree of accuracy. They reveal a creature adapted to a bipedal stance, a feature that suggests agility and perhaps a swift means of navigating its environment.
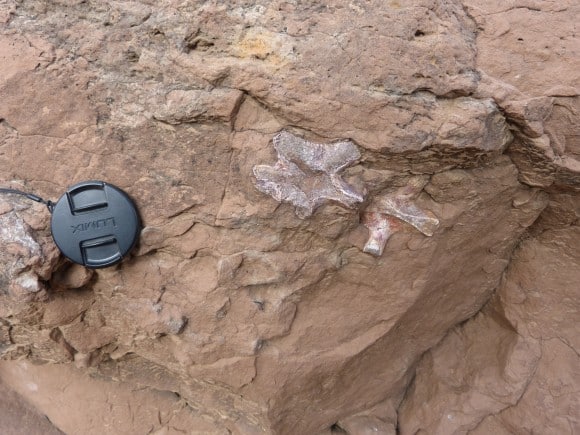 vertebrae in Clarens Formation Golden Gate National Park South Africa
vertebrae in Clarens Formation Golden Gate National Park South Africa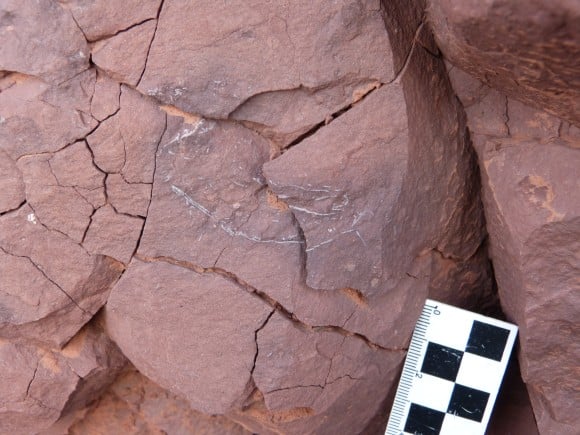 egg shell of Massospondylus, Golden Gate National Park, South Africa
egg shell of Massospondylus, Golden Gate National Park, South Africa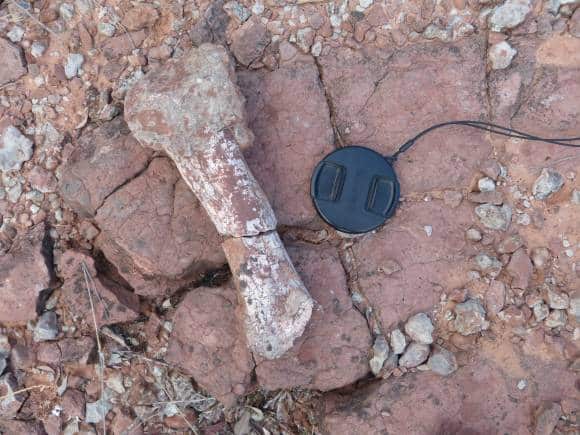 Long bone in Elliott Formation, South Africa
Long bone in Elliott Formation, South Africa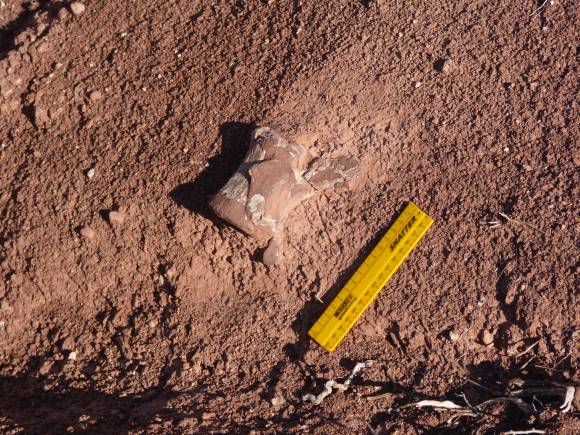 Vertebra, Elliott Formation South Africa
Vertebra, Elliott Formation South Africa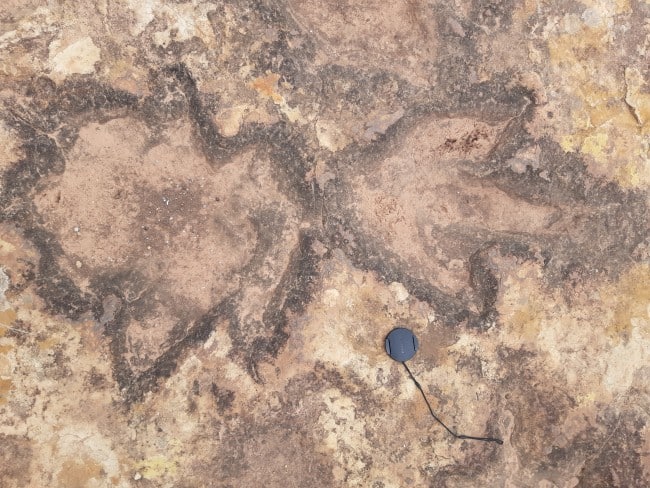 Dino tracks, Clarens Formation, Mafube Mountain Retreat site in South Africa
Dino tracks, Clarens Formation, Mafube Mountain Retreat site in South Africa
Gallery Pictures Credit: Private, Dr. Alienor
Lesothosaurus Size and Description
Lesothosaurus’s physique was streamlined for efficiency. With a lightweight frame supported by two strong hind legs, it likely moved with agility, foraging for plants. Its head, small and equipped with a beak-like mouth, was ideal for nibbling vegetation. The absence of front teeth, replaced by a horny beak, indicates a diet of soft plant material, which it could easily grasp and consume thanks to its dexterous forelimbs.
Size and Weight of Type Species
Lesothosaurus varied significantly in size, with lengths ranging from approximately 3.3 feet to an impressive 6.6 feet. This variation indicates a degree of diversity within the species, possibly related to age, sex, or even distinct ecological niches occupied by different individuals.
Despite its range in size, the overall build of Lesothosaurus was uniformly light, suggesting an animal that relied on speed rather than strength. While exact weight estimates are challenging without complete skeletal remains, the lightweight structure and size of this dinosaur imply it was a nimble creature, adept at navigating its environment with ease and efficiency.
The Ultimate Dino Quiz
Do you want to test your knowledge on dinosaurs? Then try this Ultimate Dino Quiz! Don’t worry if you get some of the answers wrong, and look at it as an opportunity to refresh and improve your knowledge!
Don’t forget to try our other games as well!
The Dinosaur in Detail
Lesothosaurus distinguishes itself through several unique features. Its dentition, for instance, is notably different from that of many other dinosaurs. The teeth, designed for grinding plant material, indicate a diet that was strictly herbivorous. This dietary preference sheds light on the ecosystem in which it thrived, suggesting a landscape abundant with ferns, cycads, and perhaps early flowering plants.
Notable specimens, including the holotypes, have contributed significantly to our understanding of Lesothosaurus. These fossils, through their preservation and the details they reveal, provide a window into the life of a dinosaur that roamed the Earth over 200 million years ago. Their study has helped paleontologists piece together the puzzle of dinosaur evolution, offering clues about how these ancient creatures adapted to their environments.
Contemporary Dinosaurs
Among Lesothosaurus’ contemporaries was Massospondylus, a behemoth when comparing the two. Stretching to lengths that Lesothosaurus could only dream of reaching. While Lesothosaurus nibbled on the low-growing foliage, Massospondylus, with its towering neck, could graze from the treetops, a dining etiquette that ensured minimal competition for meals. Yet, the presence of Massospondylus meant that Lesothosaurus had to be ever-watchful. A misplaced step in the presence of these giants could mean disaster, yet their coexistence showcased a delicate balance, where size dictated not dominance but the division of nature’s bounty.
Heterodontosaurus, roughly the same size as Lesothosaurus, added a layer of direct competition for resources. These two might have locked eyes over the same succulent plant, their diets overlapping as much as their habitats. However, Heterodontosaurus, with its unique dentition, could crunch on a variety of foods, possibly giving it an edge over our main dinosaur. This rivalry, though, was more than a battle for breakfast; it was a dynamic interaction that pushed Lesothosaurus to be quicker, smarter, and more resourceful in the face of competition.
Amidst these interactions, Lycorhinus lurked, smaller than Lesothosaurus but no less significant. This dynamic added a thrilling twist to the tale, as Lycorhinus, despite its size, could have been a formidable foe or an unexpected ally in scavenging. Their relationship was a complex dance, where size was deceptive, and survival depended on wit and agility. Lesothosaurus, navigating a world shared with creatures like Abrictosaurus, which it likely outpaced in the quest for survival, found itself in a constant game of strategy. Each dinosaur played a role in this prehistoric drama, where the prize was life itself, and the cost of failure was extinction.
Interesting Points about Lesothosaurus
- Lesothosaurus is one of the earliest known ornithopods, highlighting its importance in understanding the evolution of this dinosaur group.
- Its discovery in Lesotho marks it as one of the few dinosaurs known from this region, offering unique insights into cretaceous and jurassic life in Southern Africa.
- The efficiency of its bipedal locomotion suggests that early dinosaurs had developed sophisticated means of movement.
- The absence of front teeth and the presence of a beak-like structure indicate a specialized diet, underscoring the diversity of feeding strategies among early dinosaurs.
- Lesothosaurus’s small size challenges the common perception that all dinosaurs were massive creatures, revealing a more nuanced picture of dinosaur biodiversity.
Lesothosaurus in its Natural Habitat
Lesothosaurus, thrived in an environment that was as dynamic as it was diverse. Unraveling the world in which this dinosaur lived offers a window into a pivotal moment in Earth’s history, when ecosystems were undergoing significant transformations. This exploration into its natural habitat reveals not only the conditions of the ancient landscapes but also the interactions and adaptations of the creatures that inhabited them.
Geological Context and Climate
The fossils of Lesothosaurus have been primarily excavated from the Karoo Stormberg Group Upper Elliot and Clarens Formations, 204 to 192 million years ago (Rhaetian to Sinemurian). The Upper Elliot Formation, composed of layers of red/purple mudstone and red/white sandstone, contrasts with the Clarens Formation’s white/cream-colored sandstone. These geological layers offer clues to the climate and environmental conditions of the time. The areas’ inhabitants, including Lesothosaurus, were more lightly built. An adaptation possibly necessitated by a drier climate prevalent in Southern Africa during this epoch.
Ecosystem and Biodiversity
 Site of Ledumahadi mafube, Eliott Formation
Site of Ledumahadi mafube, Eliott Formation Clarens Formation, Golden Gate National Park, South Africa
Clarens Formation, Golden Gate National Park, South Africa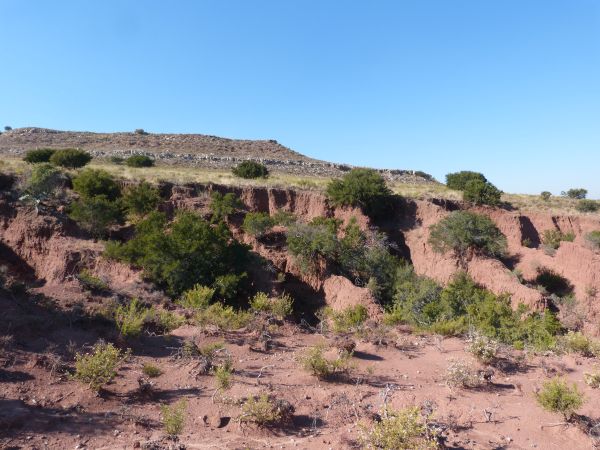 Elliott Fornation South Africa
Elliott Fornation South Africa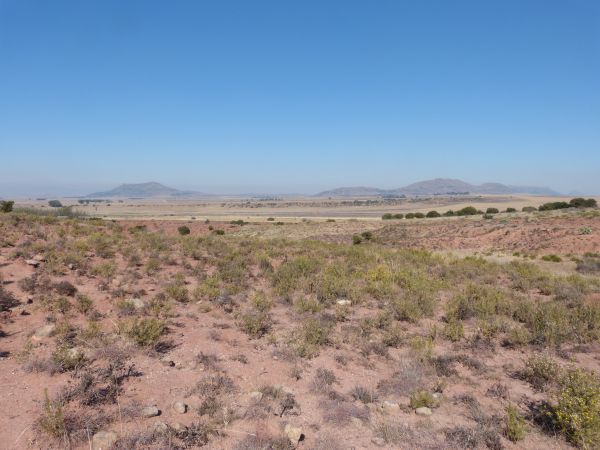 Elliott Formation South Africa landscaoe
Elliott Formation South Africa landscaoe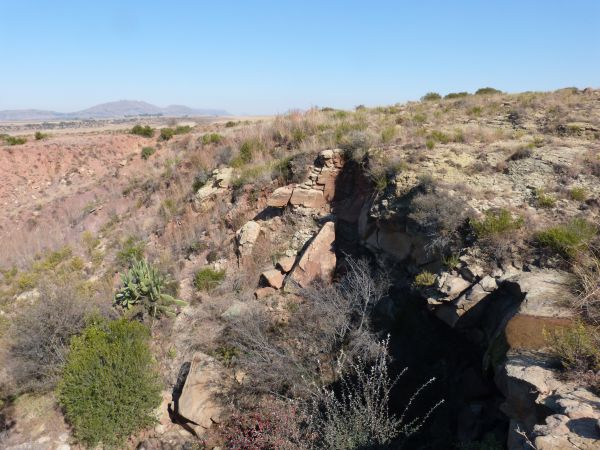 Elliott Formation South Afric rocks
Elliott Formation South Afric rocks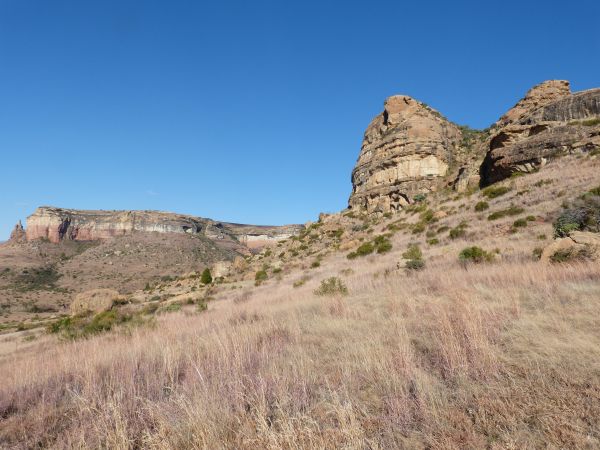 Clarens Formation, Mafube Mountain retreat site
Clarens Formation, Mafube Mountain retreat site
Credit: Private, Dr. Alienor
Both the Upper Elliot and Clarens Formations are celebrated for their rich fossil and footprint records. From temnospondyl amphibians to turtles, lepidosaurs, aetosaurs, crocodylomorphs, and non-mammal cynodonts. These formations provide a comprehensive snapshot of Early Jurassic biodiversity. The presence of other dinosaurs, such as the heterodontosaurid Heterodontosaurus, the basal sauropodomorph Massospondylus, and the theropod Megapnosaurus, alongside Lesothosaurus, paints a vivid picture of a bustling prehistoric ecosystem.
The Upper Elliot Formation is particularly notable for housing the largest known diversity of heterodontosaurids. They are a group that includes Lycorhinus, Abrictosaurus, and Pegomastax, in addition to Heterodontosaurus. This diversity suggests a complex ecosystem where niche partitioning allowed different species to coexist. Likley by exploiting separate food sources, thereby reducing competition for resources. Such ecological strategies highlight the adaptability and ecological intelligence of these ancient creatures. Moreover it ensured their survival in the varied landscapes of Late Triassic-Early Jurassic Southern Africa.
This rich tapestry of life, with its intricate interactions and evolutionary innovations, underscores Lesothosaurus’s role within its ecosystem. As a part of this diverse community, it navigated a world filled with both opportunity and challenge. Indeed a testament to the resilience and complexity of early dinosaur life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Lesothosaurus was a herbivore, feeding on a variety of plants, including ferns and cycads.
It moved on two legs, suggesting it was a fast and agile dinosaur.
It was first discovered in the Upper Elliot Formation in Lesotho.
The fossils date back to the Late Triassic-Early Jurassic Period, approximately 204 to 192 million years ago.
While it shares characteristics with other ornithopods, its unique features and early appearance in the fossil record set it apart.
Sources
The information in this article is based on various sources, drawing on scientific research, fossil evidence, and expert analysis. The aim is to provide a comprehensive and accurate overview of Lesothosaurus. However, please be aware that our understanding of dinosaurs and their world is constantly evolving as new discoveries are made.
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF03006735
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/254313592_Sereno_P_C_Lesothosaurus_Fabrosaurids_and_the_early_evolution_of_Ornithischia_Journal_of_Vertebrate_Paleontology
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4690377/
- https://academic.oup.com/zoolinnean/article/179/1/125/2870020?login=true
- https://journals.co.za/doi/abs/10.25131/sajg.123.0009
- https://journals.co.za/doi/abs/10.25131/sajg.123.0018
Article last fact checked: Joey Arboleda, 03-05-2024
Featured Image Credit: Jack Wood, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons