Stygimoloch was a herbivore that used to roam what is today North America. A genus of Pachycephalosaurid dinosaur, lit ived during the Late Cretaceous Period. It has maybe the coolest name of any dinosaur, ‘Stygimoloch‘ meaning “Demon from the river Styx”. This unique dinosaur, whose name evokes images of mythological underworlds, had some fascinating features.
Stygimoloch Key Facts
| Keyword | Fact |
|---|---|
| Stygimoloch pronunciation | STIJ-ee-MOE-lock |
| Meaning of name | Demon from the river Styx |
| Group | Pachycephalosauridae |
| Type Species | Stygimoloch spinifer |
| Diet | Herbivore |
| When it Lived | 72.1 to 66.0 MYA |
| Period | Late Cretaceous |
| Epoch | Maastrichtian to Lancian |
| Length | 10.0 to 11.0 ft |
| Height | 5.6 ft |
| Weight | 200 lbs. |
| Mobility | Moved on two legs |
| First Discovery | 1983 by Peter Galton and Hans-Dieter Sues |
| Location of first find | Montana, USA |
| First Described by | 1983 by Peter Galton |
| Holotype | UCMP 128561 |
Stygimoloch Origins, Taxonomy and Timeline
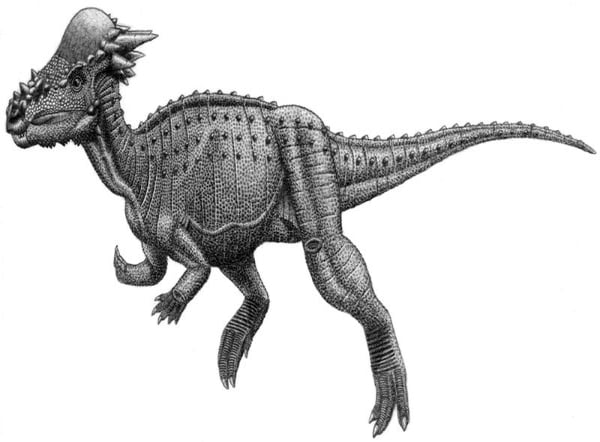
Stygimoloch, got its name, “Demon from the river Styx,” in reference to the river Styx of Greek mythology and a Canaanite Demon God, Moloch. This name reflects the dinosaur’s distinct skull features–which include long, horn-like projections and a thickened dome.
Belonging to the Pachycephalosauridae family, Stygimoloch is a part of the order Ornithischia. Its type species, Stygimoloch spinifer, is unique in its family due to its peculiar skull characteristics, in particular, all the horns it sported in life.
While it is recognized as part of the Pachycephalosauridae family, some paleontologists have suggested that it was indeed a young Pachycephalosaurus, rather than a separaste genus. This is still up for debate, but does make it somewhat controversial.
This herbivore thrived during the end of the Late Cretaceous period, specifically during the Maastrichtian to Lancian epochs, some 72 to 66 million years ago. This period, known for its rich biodiversity, was the last part of the Mesozoic Era and often referred to as the Age of Dinosaurs.
Listen to Pronunciation
Discovery & Fossil Evidence
Stygimoloch fossils were first discovered in 1983 by Peter Galton and Hans-Dieter Sues. The initial find, made in Montana, USA consisted of a partial skull, which is now considered the holotype of this dinosaur. The unique features of the skull, particularly the horn-like projections and the thickened dome, led to the identification of a new genus.
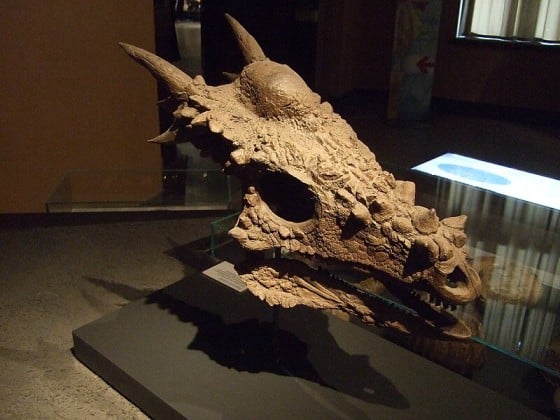

Since the first discovery, several other specimens have been found, contributing to our understanding of this unique dinosaur. These fossils primarily consist of skull fragments but have provided valuable insights into the dinosaur’s physical characteristics and lifestyle.
The degree of preservation of these fossils varies, with some specimens being more complete than others. Notable specimens include those that showcase the dinosaur’s distinct skull features, which have been instrumental in understanding its place in the dinosaur taxonomy.
Stygimoloch Size and Description
This was a bipedal dinosaur, meaning it moved on two legs. Its most striking feature was its skull, which had a thickened dome and long, horn-like projections. These projections, along with its small size and herbivorous diet, make it a unique member of the dinosaur kingdom.
The body of the Stygimoloch was likely compact with a long tail for balance. Its limbs were well-adapted for bipedal movement with the hind limbs being significantly larger than the forelimbs. The skin of the Stygimoloch is not well-known but, like other dinosaurs, it was likely covered in scales.
Size and Weight of Type Species
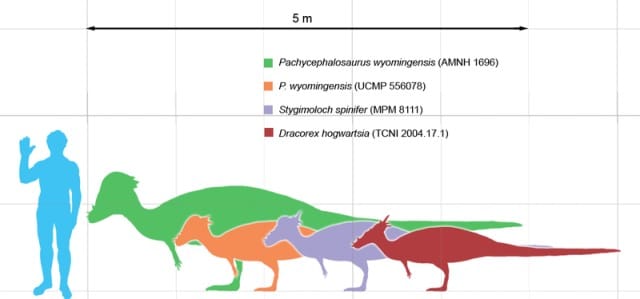
The exact size and weight are not well-documented due to the limited number of fossils available. However, based on the size of its skull and comparisons with related species, it is estimated that it was a small dinosaur. Its estimated that Stygimoloch was around 10 to 11 feet in length, around 5 feet tall at the hips, and weighed about 180-200 lbs.
These estimates, while not precise, give us a general idea of the size and stature of this unique dinosaur. It’s important to remember that these are estimates and the actual size and weight could have varied.
The Dinosaur in Detail
Stygimoloch and its unique skull stands out among its dinosaur counterparts. The thickened dome and horn-like projections on its skull are not just distinctive but they also hint at the dinosaur’s adaptability and survival instincts.
The thickened dome on the skull, for instance, could have served multiple purposes. It could have been used for display–to attract mates or intimidate rivals. It could also have been used in combat, with Stygimoloch ramming its head into opponents. The horn-like projections on the Stygimoloch’s skull add another layer of intrigue to this dinosaur. These projections, while not true horns, could have served similar purposes–for display, combat, or both.
Notable specimens of Stygimoloch, such as the holotype skull, have provided valuable insights into this dinosaur’s life. These specimens showcase the dinosaur’s distinct characteristics and offer a glimpse into its behavior and lifestyle.
Stygimoloch in its Natural Habitat
Like other dinosaurs of its time, this creature lived in a world vastly different from ours. The Late Cretaceous period was characterized by warm climates and diverse ecosystems. North America had been split by an interior seaway and was known as Laramidia to the west and Appalachia to the east. The Stygimoloch made its home on Laramidia.
This was an herbivore that fed on the abundant vegetation of its time. Its diet likely consisted of a variety of plants, including ferns, cycads, and possibly even flowering plants, which were just beginning to diversify during the Late Cretaceous.
Being a smaller bipedal dinosaur, this was likely a fast and agile creature. This would have been beneficial in both foraging for food and evading predators. Its unique skull features, particularly the thickened dome and horn-like projections, suggest that it could have been quite aggressive and possibly used its head for combat and defense.
Its social behavior is not well-known but it is possible that it lived in small groups or herds. This would have provided protection against predators and increased the chances of finding food.
This herbivorous dinosaur would have played a significant role in its ecosystem. Its feeding habits could have influenced the distribution of plant species, while its aggressive behavior could have affected the behavior of other dinosaurs in its environment.
Interesting Points about Stygimoloch
- The name Stygimoloch, which translates to “Demon from the river Styx,” is a reference to the river Styx of Greek mythology and the Hebrew word Moloch, often associated with a Canaanite god.
- It is known primarily from skull fragments which showcase its unique skull features–a thickened dome and horn-like projections.
- Despite being an herbivore, the skull features suggest that it could have been quite aggressive and may have used its head for combat or defense.
- It lived during the Late Cretaceous period, the last segment of the Mesozoic Era often referred to as the “Age of Dinosaurs.”
Contemporary Dinosaurs
Some of the Laramidian dinosaurs that could be found alongside the Stygimoloch include Edmontosaurus, Tyrannosaurus, Triceratops, and Ankylosaurus.
The larger Edmontosaurus was an herbivore like Stygimoloch and might have been a competitor for plant resources. Yet, their differing feeding habits could have allowed them to coexist without direct conflict. The specialized diet of the Stygimoloch might have meant it occupied a different ecological niche, reducing competition.
Triceratops and Ankylosaurus, both larger and heavily armored herbivores, present a stark contrast to the relatively smaller Stygimoloch. Their presence paints a picture of a world where size and strength were crucial for survival.
Then, there was Tyrannosaurus, a predator of terrifying proportions. Stygimoloch, despite its smaller size, was no easy prey. Its thick skull and the horn-like structures could have been used in defense, making any predatory attempt a risky endeavor. This dynamic might have added a layer of tension to their coexistence. Yet, Stygimoloch found its place in this world, a testament to the diverse ways life adapted and thrived in the prehistoric era.
List of All Dinosaurs
We have created a list of all dinosaurs we have covered here, sorted across the seven main groups of dinosaurs. We also include information about their type of diet, (omnivore, herbivore or carnivore) and the time they lived.
Frequently Asked Questions
The name translates to “Demon from the river Styx,” a reference to the river Styx of Greek mythology and the Hebrew word Moloch, often associated with a Canaanite god.
It lived during the Late Cretaceous period, specifically around 72.1 to 66.0 million years ago.
This was an herbivore, feeding on a variety of plants.
It was first discovered in 1983 by Peter Galton and Hans-Dieter Sues. The initial find was made in Montana, USA.
It is known for its unique skull features, which include a thickened dome and long, horn-like projections.
Sources
- https://digitallibrary.amnh.org/handle/2246/387?show=full
- https://www.jstor.org/stable/4523906
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/08912963.2020.1793979?journalCode=ghbi20
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/232692237_Revision_of_the_dinosaur_Stegoceras_Lambe_Ornithischia_Pachycephalosauridae
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/240625747_A_taxonomic_review_of_the_Pachycephalosauridae_Dinosauria_Ornithischia
This article was last fact checked:Joey Arboleda, 06-13-2023
Featured Image Credit: Jordan Mallon, CC BY-SA 2.5, via Wikimedia Commons
