Torosaurus was a cerstopsian herbivore whose name means “perforated lizard.” It roamed the earth during the Late Cretaceous Period. With its distinctive frilled head and large size, this dinosaur is a fascinating subject of study for paleontologists and hobbyists alike.
Torosaurus is a symbol of the incredible adaptability and survival instincts that dinosaurs possessed. Its unique features, such as its large frill and horns, not only set it apart from other dinosaurs but also reflect its adaptability to its environment. This dinosaur is an example to the power of evolution and the enduring mystery of the dinosaur era.
Key Facts
| Keyword | Fact |
|---|---|
| Torosaurus pronunciation | TOR-o-SAWR-us |
| Meaning of name | Perforated Lizard |
| Group | Ceratopsids |
| Type Species | Torosaurus latus |
| Diet | Herbivore |
| When it Lived | 72.1 to 66.0 MYA |
| Period | Late Cretaceous |
| Epoch | Maastrichtian to Late/Upper Maastrichtian |
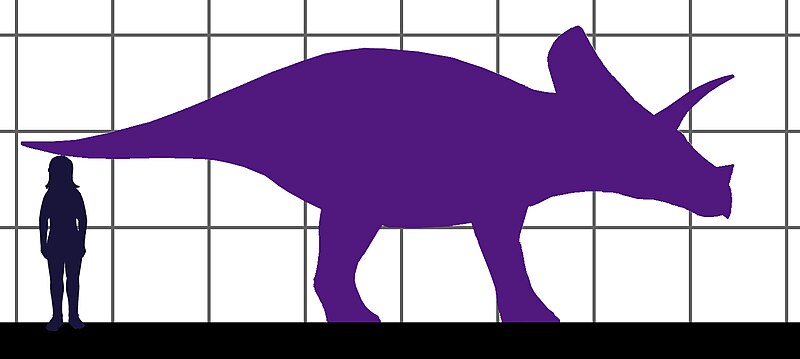
| Length | 25.0 ft |
| Height | 8.0 ft at hips |
| Weight | 4.4 to 6.6 tons |
| Mobility | Moved on all four |
| First Discovery | 1891 by Othniel Charles Marsh |
| Location of first find | Wyoming, USA |
| Described by | 1891 by Othniel Charles Marsh |
| Holotype | YPM 1830 |
Torosaurus Taxonomy and Timeline
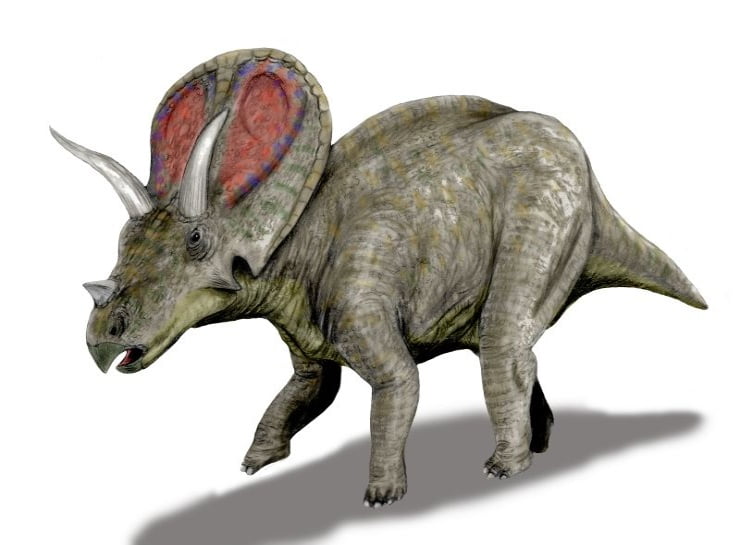

The name, “Perforated lizard” was given to it due to the unique nature of this dinosaur’s skull, having a large frill with two openings in the bone structure. The name Torosaurus is derived from the Greek words “toreo“, meaning perforated, and “saurus“, meaning lizard.
Taxonomically, Torosaurus belongs to the Ceratopsidae family–a group of herbivorous dinosaurs known for their distinctive horns and frills. Within this family, it is part of the Chasmosaurinae subfamily and the species of this genus include Torosaurus latus and Torosaurus utahensis.
The timeline of this dinosaur is set at the very end of the Late Cretaceous period. This was a time of significant change and evolution, with the earth’s continents moving closer to their current positions and the climate becoming cooler and drier.
Discovery & Fossil Evidence
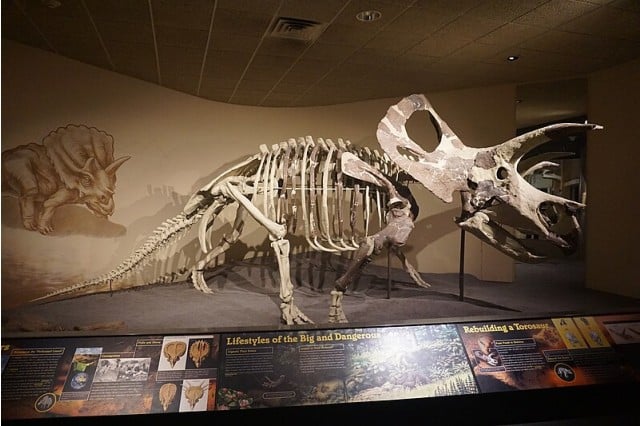
The first discovery of Torosaurus fossil remains was made in 1891 by the renowned paleontologist Othniel Charles Marsh. The fossils were found in Wyoming, USA and included a nearly complete skull, which allowed Marsh to identify Torosaurus as a new genus of dinosaur. Since this initial discovery, additional fossils have been found in other parts of the USA including Montana, South Dakota, and possibly Texas and Utah.

These later finds have provided valuable insights into the life and characteristics of this dinosaur. For instance, the discovery of multiple fossils in close proximity to each other suggests that these dinosaurs may have lived in social groups. The fossils also reveal that it had the largest display crest of any ceratopsian, a feature that was likely used for display and possibly for defense.
Torosaurus Size and Description
With its distinctive horns and large frill, this giant was a sight to behold. It is known for its large size and distinctive physical features. Its sturdy body, large frill, and sharp horns helped it navigate its environment with ease. These adaptations not only helped to keep it safe from predators but also potentially allowed it to communicate with others of its kind, possibly as part of mating selection.
Size and Weight of Type Species
Estimates of its length goes as far as it reaching up to 25 feet. Its height at the hips was likely around 8 feet. The weight is harder to estimate but it was likely in the range of several tons. These estimates are based on the size of the fossils that have been found, as well as comparisons with similar ceratopsian dinos. However, it’s important to note that these are estimates and the actual size and weight could have varied.
The Dinosaur in Detail
Torosaurus is a bit of a marvel of prehistoric engineering. Its body was robust and sturdy to support its large size. The head was adorned with a large frill and two long, forward-facing horns above its eyes, reminiscent of a bull’s horns. Its neck was strong and muscular, capable of supporting the weight of its large head. It had a long tail that likely served as a counterbalance to its heavy front body. Its skin was likely rough and scaly, similar to that of modern reptiles. This was a quadruped that moved on all four limbs.
Its large frill and horns are not just distinctive features, but also key adaptations that likely played a crucial role in its survival. The frill, for instance, was likely used for display purposes, to intimidate rivals, or attract mates. The horns, on the other hand, could have been used for defense against predators.
One of the most notable specimens of Torosaurus is the holotype YPM 1830. This specimen, discovered by Othniel Charles Marsh in 1891, includes a nearly complete skull and has provided invaluable insights into the anatomy and characteristics of this dinosaur. The study of this and other specimens has greatly contributed to our understanding of this fascinating dinosaur.
Torosaurus in its Natural Habitat

Torosaurus lived during the Late Cretaceous period in a time when the earth’s climate was becoming cooler and drier. The landscape was likely dominated by open forests and plains, with a diverse range of plant life. As an herbivore, Torosaurus would have taken advantage of the abundant vegetation, using its sharp beak to tear off leaves and branches.
It was a quadruped, moving on all four limbs. This mode of locomotion and its large size suggests that Torosaurus was a slow-moving dinosaur. Additionally, its size would have offered some protection against predators. It likely had a relatively long lifespan although exact estimates are difficult to determine.
The social behavior of this dinosaur is a subject of ongoing research. Some evidence, such as the discovery of multiple fossils in close proximity to each other, suggests that they may have lived in social groups. However, more research is needed to confirm this hypothesis.
Interesting Points about Torosaurus
- It had the largest skull of any land animal known to science, measuring in at over 8 feet long.
- There is an ongoing debate among paleontologists about whether the Torosaurus is a distinct species or simply a mature form of the Triceratops.
- It had a large frill with two large holes in it, a feature that is unique among ceratopsians.
- The Torosaurus likely lived near the coast of North America, suggesting it may have inhabited a variety of environments–from coastal areas to inland plains.
- A life-size statue of the Torosaurus can be seen at the Peabody Museum of Natural History.
Contemporary Dinosaurs
The prehistoric world of Torosaurus would have been unrecognizable today. For example, North America was not one continent but two–split down the middle by an inland sea. The western continent, Laramidia, is where this dinosaur roamed alongside its contemporaries. Among these were Triceratops, Tyrannosaurus, and Dakotaraptor, each playing a unique role in the intricate ballet of existence that unfolded in this bygone era.
Triceratops, a fellow ceratopsid, was a frightening presence in its own right. Its size was comparable to that of Torosaurus, and one can imagine these two titans moving through their shared environment–their paths occasionally crossing in a silent acknowledgement of their shared lineage. Yet, their coexistence was not without its challenges. Tyrannosaurus, a predator of terrifying proportions, loomed large in this prehistoric landscape. Despite its size and formidable frill, these herbivores would have had to navigate this perilous terrain constantly aware of the lurking threat of Tyrannosaurus.
Adding another layer of complexity to this dynamic was Dakotaraptor. Smaller than Torosaurus and Triceratops but no less significant, Dakotaraptor was a nimble hunter. Its agility was a stark contrast to the lumbering gait of its larger contemporaries. Torosaurus was not the likely prey of a Dakotaraptor and would have shared the landscape with this agile predator. Through this lens, we gain a deeper understanding of Torosaurus, not as a solitary figure, but as a part of a vibrant and complex community of dinosaurs.
List of All Dinosaurs
We have created a list of all dinosaurs we have covered here, sorted across the seven main groups of dinosaurs. We also include information about their type of diet, (omnivore, herbivore or carnivore) and the time they lived.
Frequently Asked Questions
The name translates to “perforated lizard”, derived from the Greek word “toreo“, meaning perforated, and “saurus“, meaning lizard.
It lived during the Late Cretaceous period, specifically between 72.1 to 66.0 million years ago.
It was an herbivore, meaning it ate plants. It likely grazed on a variety of vegetation available during its time.
The first fossils were found in Wyoming, USA. Additional fossils have been found in Montana, South Dakota, and possibly Texas and Utah.
There is an ongoing debate among paleontologists about whether the Torosaurus is a distinct species or simply a mature form of the Triceratops.
Sources
- https://marsh.dinodb.com/marsh/Marsh%201891%20-%20Notice%20of%20new%20vertebrate%20fossils.pdf
- https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0028705
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0195667114001293
- https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0032623
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11434-009-3614-5
Please note that the information in this article is based on various sources, drawing on scientific research, fossil evidence, and expert analysis. The aim is to provide a comprehensive and accurate overview of the Torosaurus, but please be aware that our understanding of dinosaurs and their world is constantly evolving as new discoveries are made.
This article was last fact checked: Joey Arboleda,06-14-2023