The Tyrannosaurus rex, often simply referred to as T. rex or T-Rex, is a symbol of power and dominance in the world of dinosaurs. Its name, derived from the Greek words for ‘tyrant’ and ‘lizard’, and the Latin word for ‘king’, perfectly encapsulates the awe-inspiring presence of this prehistoric creature.
In the realm of design, the T-Rex stands as a testament to nature’s ingenuity. Its massive size, powerful jaws, and robust build are all elements of a design that was honed over millions of years. This dinosaur, like a meticulously crafted piece of technology, was built for a specific purpose–to be the apex predator of its time.
Tyrannosaurus rex Key Facts
| Keyword | Fact |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | tie-RAN-oh-SAWR-us |
| Meaning of name | Tyrant Lizard King |
| Group | Theropods |
| Type Species | Tyrannosaurus rex |
| Diet | Carnivore |
| When it Lived | 72.1 to 66.0 MYA |
| Period | Late Cretaceous |
| Epoch | Maastrichtian to Lancian |
| Length | 40.0 ft |
| Height | 20.0 ft |
| Weight | 15.4 to 14.0 tons |
| Mobility | Moved on two legs |
| First Discovery | 1874 by Arthur Lake |
| Location of first find | Colorado, USA |
| First Described by | 1905 by Henry Fairfield Osborn |
| Holotype | MOR 008 |
Tyrannosaurus Origins, Taxonomy and Timeline
The name Tyrannosaurus rex is as grand as the creature itself. It translates to ‘Tyrant Lizard King’, a fitting title for a dinosaur that was one of the largest land carnivores of all time. The genus name, Tyrannosaurus, comes from the Greek words ‘tyrannos’ (tyrant) and ‘sauros’ (lizard). The species name, rex, is Latin for ‘king’.
In terms of taxonomy, the T-Rex belongs to the Theropoda group, specifically the family Tyrannosauridae, and the species T. rex. This classification places it among the most fearsome predators that ever walked the Earth. While Tyrannosaurus rex is often referred to as the only species of Tyrannosaurus, the closely related Tarbosaurus bataar is occasionally placed in the same genus and thus sometimes referred to as Tyrannosaurus bataar.
This carnivorous dinosaur lived during the Late Cretaceous period, specifically at the very end. This was a time when the Earth was warm and sea levels were high, creating a landscape of shallow inland seas and lush vegetation in North America.
Listen to Pronunciation
Discovery & Fossil Evidence
Arthur Laek discovered the the first fossil in 1874. This discovery of teeth near Golden, Colorado marked the beginning of our understanding of this magnificent creature.

Since then, numerous other fossils have been found across North America. These fossils, which include bones, teeth, and even footprints, have provided invaluable insights into its size, diet, and behavior.
One of the most notable specimens is ‘Sue’, a nearly complete T-Rex skeleton that was discovered in 1990. At 40 feet long and 13 feet tall at the hips, Sue is the largest and most complete Tyrannosaurus skeleton ever found.
Tyrannosaurus Size and Description
This was an iconic symbol of the dinosaur age and a creature that commands attention. Its massive size and formidable features have made it a subject of fascination for scientists and dinosaur enthusiasts alike. Let’s delve into the physical characteristics and dimensions of this prehistoric titan.
Short description of Tyrannosaurus
It was a bipedal dinosaur, moving on two robust legs while its upper limbs were relatively small. Despite their size, these arms were incredibly strong and ended in two clawed fingers. The T-Rex’s head was large and equipped with a set of powerful jaws, housing sharp, serrated teeth that could reach up to 12 inches in length. Its long, heavy tail served as a counterbalance to its large head and torso and provided stability as it moved.
Size and Weight of Type Species
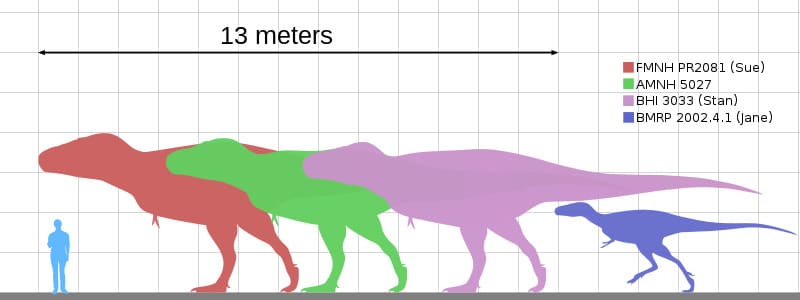
This was one of the largest land carnivores to have ever lived. Adults could reach lengths of up to 40 feet and stand up to 20 feet tall. Their weight is estimated to have been between 5.4 to 14 metric tons, making them heavier than an African elephant.
However, these figures are estimates and actual sizes may have varied. For instance, the specimen known as ‘Sue’ is the largest and most complete fossil discovered to date, measuring 40 feet in length. On the other hand, some smaller adult specimens have also been found that suggest a possible range in size and weight among them.
Tyrannosaurus Games
If you want to test your knowledge about Tyrannosaurus, here is a fun quiz you can play. Don’t worry if you don’t get all questions right, it is a learning opportunity! Have fun!
The Dinosaur in Detail
The Tyrannosaurus is more than just a large dinosaur; it’s a marvel of natural engineering. Its unique features and adaptations set it apart from other dinosaurs and underscore its role as a top predator in its ecosystem.
It had a solidly built body with a robust skeletal structure. The skin is believed to have been covered in scales, and recent discoveries suggest the possibility of feathers–particularly in younger individuals. However, the extent and location of feather coverage remain subjects of ongoing research. Its long tail was sturdy and an important factor in allowing it to move quickly and capably by providing a counterbalance to its large head.
One of its most distinctive features is its teeth. Unlike most theropods, which have blade-like teeth, it had conical teeth that were designed for crushing rather than slicing. This adaptation allowed it to bite through bone, making it one of the few predators capable of fully utilizing its prey.
Another notable feature is its keen sense of smell. Its olfactory bulbs were highly developed, suggesting that it relied heavily on its sense of smell to locate prey. This, combined with its binocular vision, made the T-Rex an efficient and deadly hunter.
Tyrannosaurus Rex Illustration Sketch
The Tyrannosaurus in its Natural Habitat
This predator lived during the Late Cretaceous period, a time when the Earth was warmer than it is today, with high sea levels and a landscape dotted with shallow inland seas and dense forests. At the time, North America had been split into two paleocontinents by an interior seaway. The Tyrannosaurus could be found on the western half, known as Laramidia. This environment was home to a diverse array of plant and animal life that provided it with ample hunting opportunities.
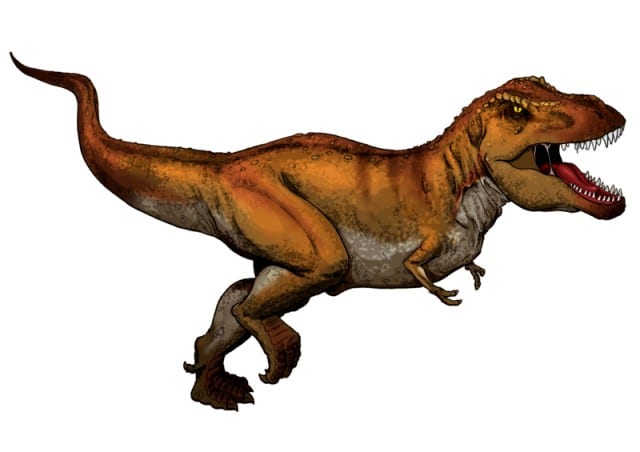

It was a carnivore and its diet primarily consisted of other dinosaurs. Its powerful jaws and sharp teeth allowed it to take down large prey and crush bones after its keen senses of sight and smell helped it locate food. It was likely both a predator and a scavenger that used its size and strength to dominate its environment.
Its role in its ecosystem was significant. As an apex predator, it played a crucial part in maintaining the balance of species in its environment. Its hunting activities would have influenced the behavior and distribution of other animals, shaping the landscape around it.
Interesting Points about Tyrannosaurus
- It had one of the strongest bites of any land animal that ever lived. Its bite force could reach up to 12,800 pounds, equivalent to the weight of a medium-sized elephant.
- Despite its massive size, it was likely quite agile, with estimates suggesting a top speed of up to 25 miles per hour.
- The arms, while small relative to its body size, were incredibly strong and could lift weights of up to 450 pounds.
- It is believed to have had the largest brain of any carnivorous dinosaur, suggesting high intelligence and possibly complex behaviors.
- The discovery of soft tissue in a T-Rex fossil in 2005 provided unprecedented insight into its biology, including evidence of medullary tissue, which is found only in female birds preparing to lay eggs.
Contemporary Dinosaurs
This creature of popular renown found itself in a dynamic ecosystem teeming with diverse life forms. Among these Laramidian dinosaurs were the Triceratops, Edmontosaurus, Dakotaraptor, and Ankylosaurus. Each of these North American dinosaurs played their own role alongside the Tyrannosaurus to create the dynamic environment of the Late Cretaceous.
The distinctive three-horned face of the Triceratops was a sight to behold. Its size, though smaller than the Tyrannosaurus, was no less impressive. The relationship between these two was likely one of predator and prey, a testament to the harsh realities of survival in the Cretaceous period. Yet, the Triceratops was far from defenseless and could use its large horns and frill potentially as formidable deterrents to the mighty Tyrannosaurus.
The heavily armored body of the Ankylosaurus shows another adaptation of the defense systems of herbivores at this time. Despite being considerably smaller, it was far from an easy target. Its unique defensive adaptations could have posed a significant challenge to the Tyrannosaurus, turning a potential predator-prey interaction into a tense standoff.
The Edmontosaurus was another herbivore, its diet consisting of the abundant plant life of the era. Lacking the obvious defense mechanisms of the Triceratops and Ankylosaurus, its coexistence with the Tyrannosaurus paints a picture of a constant game of hide and seek played out in the lush prehistoric landscapes.
The Dakotaraptor, smaller yet no less fearsome, adds another layer of complexity to this narrative. As a fellow predator, it might have competed with the Tyrannosaurus for the same prey and added a layer of tension to their coexistence. In this intricate web of life, the Tyrannosaurus, Triceratops, Edmontosaurus, Dakotaraptor, and Ankylosaurus each played their part, their lives intertwined in a complex dance of survival, competition, and coexistence.
List of All Dinosaurs
We have created a list of all dinosaurs we have covered here, sorted across the seven main groups of dinosaurs. We also include information about their type of diet, (omnivore, herbivore or carnivore) and the time they lived.
Frequently Asked Questions
This was one of the largest land carnivores, reaching lengths of up to 40 feet and standing up to 20 feet tall. Its weight is estimated to have been between 5.4 to 14 metric tons.
It was a carnivore and its diet primarily consisted of other dinosaurs. Its powerful jaws and sharp teeth allowed it to take down large prey and crush bones. It may have also scavenged on carcasses between kills.
It was a bipedal dinosaur, meaning it moved on two legs. Its long, heavy tail served as a counterbalance to its large head and torso, providing stability as it moved.
It lived during the Late Cretaceous period, specifically between 72.1 to 66.0 million years ago. This was during the end of the Age of Dinosaurs.
Fossils have been found primarily in North America with the first discovery made in Colorado, USA.
Arthur Lake found the first fossil in 1874.
Sources
- https://digitallibrary.amnh.org/bitstream/handle/2246/1464//v2/dspace/ingest/pdfSource/bul/B021a14.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
- https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/10.1098/rsos.180826
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0195667115301452
- https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0137709
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24869965/
Article last fact checked: Joey Arboleda,06-13-2023
Featured Image Credit: Copyright (c) Thedinosaurs.org
