In the grand tapestry of prehistoric life, few creatures capture the imagination quite like the Velociraptor. This dinosaur, whose name means ‘swift thief’, embodies a unique blend of agility, cunning, and raw predatory instinct. Its legacy is etched in the fossil record and offers a glimpse into a world that thrived over 70 million years ago.
The Velociraptor hailed from what is now Central Asia and was a key player in the Late Cretaceous period. Its existence, while fleeting in the grand scheme of geological time, left an indelible mark on our understanding of dinosaur behavior and evolution. This creature was small in stature but large in its cultural impact and continues to fascinate and inspire us today.
Velociraptor Key Facts
| Keyword | Fact |
|---|---|
| Velociraptor pronunciation | vel-OSS-ee-rap-tor |
| Meaning of name | Swift thief |
| Group | Theropoda |
| Type Species | Velociraptor mongoliensis |
| Diet | Carnivorous |
| When it Lived | Late Cretaceous |
| Epoch | Coniacian to Campanian |
| Length | 4.9–6.8 ft |
| Height | approximately 1.6 ft high at the hips |
| Weight | 30-45lbs |
| Mobility | Moved on two legs |
| First Discovery | 1923 by Peter Kaisen |
| Location of first find | Djadochta Formation, Gobi Desert, Mongolia |
| First Described by | 1924 by Henry Fairfield Osborn |
| Holotype | AMNH 6515 |
Velociraptor Origins, Taxonomy and Timeline
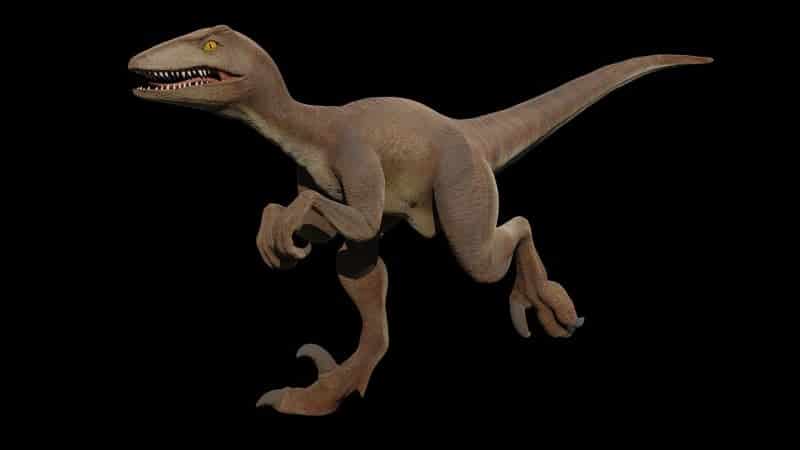

The name of the Velociraptor translates to ‘swift thief’ and is an example of the dynamism and diversity of life in the Late Cretaceous period. The name is derived from the Latin words ‘velox’, meaning swift, and ‘raptor’ meaning thief/robber/plunderer. This aptly describes the dinosaur’s predatory nature and agile hunting style.
Taxonomically, the Velociraptor belongs to the Theropoda group, a clade of bipedal dinosaurs. Within this group, it is a member of the family Dromaeosauridae, known for their distinctive sickle-shaped claws and keen predatory instincts. Velociraptor mongoliensis is the type species for this genus and is named as a reference to its initial discovery in Mongolia.
The Velociraptor thrived during the Late Cretaceous period. This was a time of significant change and diversification in the dinosaur world, with new species emerging and old ones fading away. With its unique adaptations and hunting prowess, it was a key player in this dynamic ecosystem.
Listen to Pronunciation
Fossil Evidence
The first fossil was discovered in 1923 by Peter Kaisen in the Mongolian Gobi Desert. This initial find was a crushed but nearly complete skull and a set of powerful, sickle-shaped claws that sparked a wave of interest in this previously unknown dinosaur. It was formally described a year later in 1924 by Henry Fairfield Osborn, the then-president of the American Museum of Natural History.
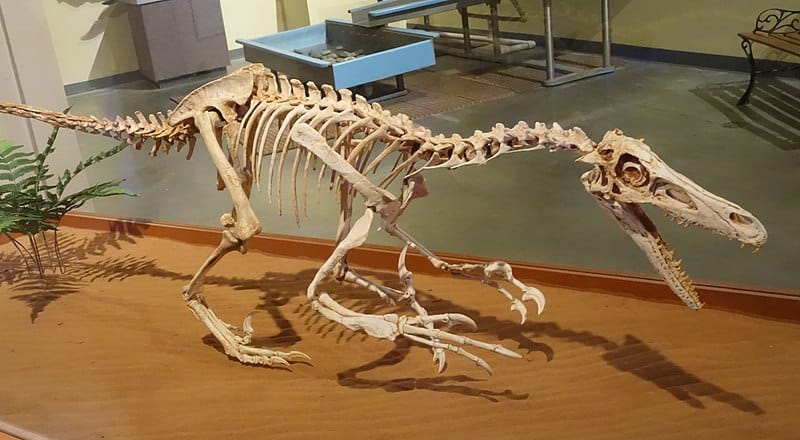

Since that initial discovery, numerous other fossils have been unearthed, primarily in the Gobi Desert and Alberta but also in locations as far-flung as Tajikistan. These fossils range from partial skeletons to individual bones and footprints and have provided a wealth of information about this dinosaur’s anatomy, behavior, and environment.
These fossils are notable for their exceptional preservation. Many specimens include well-preserved skulls, which have provided invaluable insights into the dinosaur’s sensory capabilities and feeding habits. The holotype specimen, AMNH 6515, is particularly noteworthy for its completeness and the detail it offers into this dinosaur’s anatomy.
Velociraptor Size and Description
Despite its fearsome reputation, this was not a large dinosaur. Its size and physical characteristics, however, were perfectly suited to its lifestyle and environment.
Short description of Velociraptor
The Velociraptor was a bipedal dinosaur that moved swiftly on two legs. Its body was streamlined with a long, stiff tail that provided balance and stability. The head was relatively small and equipped with sharp, serrated teeth and large, forward-facing eyes that suggest it had excellent vision. Its most distinctive feature was the large, sickle-shaped claw on each foot that it likely used to capture and kill its prey.
Its arms were long and flexible, tipped with three clawed fingers that could have been used to grasp prey or objects. Despite its small size, it was a formidable predator that was equipped with the tools and adaptations necessary to survive in its harsh, competitive environment.
Size and Weight of Type Species
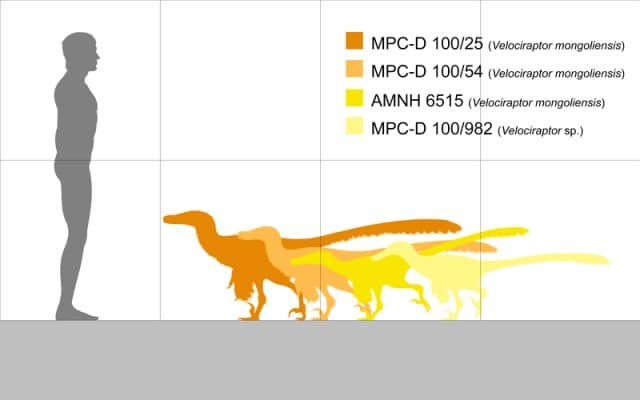
According to the most recent estimations, the Velociraptor was smaller than some of its dromaeosaurid relatives, reaching a length of 4.9–6.8 ft and weighing aroun 30-45lbs. This size estimate, while smaller than the towering giants often associated with the dinosaur world, does not diminish its significance or its role as a skilled predator.
Velociraptor Games
If you want to test your knowledge about Velociraptor, here is a fun quiz you can play. Don’t worry if you don’t get all questions right, it is a learning opportunity! Have fun!
Don’t forget to try our other games as well!
The Dinosaur in Detail
While not the largest dinosaur, this was certainly one of the most distinctive. Its unique features, from its sickle-shaped claws to its feathered body, set it apart from other dinosaurs and reflect its adaptability and survival instincts.
One of its most notable features was the large, sickle-shaped claw on each foot. This claw could reach lengths of up to 6.5 cm (2.6 inches) and was likely a key tool in its hunting arsenal. It may have been used to slash at prey, pin it down, or deliver a fatal blow. This claw, combined with the Velociraptor’s speed, agility, and the grasping claws on its hands, made it a formidable predator. Its skin was likely covered in feathers–a feature shared with many other theropods and a clear link to its bird-like descendants.
The tail was stiffened by elongated bony structures and was another key adaptation. This tail would have provided balance and stability, particularly when the dinosaur was running or maneuvering at high speeds. It may also have played a role in communication or display behaviors, although this is purely speculative.
Velociraptor Illustration Sketch
The Velociraptor in its Natural Habitat
This carnivorous dinosaur inhabited what is now Central and Eastern Asia during the Late Cretaceous period. This was a time of significant change with shifting climates and landscapes that presented both challenges and opportunities for the dinosaurs that lived during this time.
The environment in which the Velociraptor lived was likely arid, with sparse vegetation and a harsh climate. Despite these challenging conditions, it was a successful predator. It used its speed, agility, and cunning to hunt down smaller herbivorous dinosaurs and other prey. Its diet was strictly carnivorous and it likely relied on its sharp teeth and large, sickle-shaped claws to capture and kill its prey.

Its keen senses–especially its excellent vision–would have been crucial in its harsh environment. These senses would have made it a formidable hunter when combined with its speed and agility. It’s also possible that the Velociraptor was a social creature that hunted in packs to take down larger prey, although this is still a topic of debate among paleontologists.
Interesting Points about Velociraptor
- Despite its portrayal in popular media, the Velociraptor was actually about the size of a turkey.
- It likely had feathers–a feature that links it to modern birds.
- The large, sickle-shaped claw on each foot was likely a key tool in its hunting arsenal.
- The skulls found show evidence of large, forward-facing eyes that hint at its excellent vision.
- It has been found across Central, including places such as Mongolia and Tajikistan.
Contemporary Dinosaurs
This creature of cunning and agility shared its world with a diverse array of contemporaries. Among these were Asian dinosaurs like Protoceratops, Oviraptor, Pinacosaurus, and Gallimimus. Each of these dinosaurs can be compared and contrasted with the Velociraptor. Together it paints a more complete picture of its environment.
The Protoceratops, an herbivore considerably smaller than the Velociraptor, might have been a common sight. This dinosaur could have been a potential prey for the Velociraptor. The predator-prey relationship between these two species paints a vivid picture of the survival challenges that marked the Velociraptor’s existence.
The Pinacosaurus and Gallimimus, on the other hand, offer a contrast to the Velociraptor’s narrative. The armored Pinacosaurus would have been a formidable presence. Indeed its body was a stark contrast to the sleek, agile form of the Velociraptor. The Gallimimus, with its ostrich-like build and suspected speed, presents a different kind of contemporary.
There was also the Oviraptor, a dinosaur whose name means ‘egg thief’. With the Velociraptor and Oviraptor cohabiting the same environment, one can imagine the possible encounters between these two. The Oviraptor potentially competed with the Velociraptor for the same resources, adding another layer of complexity to the Velociraptor’s story.
List of All Dinosaurs
We have created a list of all dinosaurs we have covered here, sorted across the seven main groups of dinosaurs. We also include information about their type of diet, (omnivore, herbivore or carnivore) and the time they lived.
Frequently Asked Questions
The name translates to ‘swift thief, reflecting its speed and predatory nature.
It lived during the Late Cretaceous period, specifically between 75 to 71 million years ago.
It was a carnivore that fed on smaller herbivorous dinosaurs and other prey.
The first fossil was discovered in the Gobi Desert in Mongolia in 1923. Later finds have been uncovered in Central Asia.
Despite its portrayal in popular media, the Velociraptor was actually about the size of a turkey. Reaching a length of only 4.9–6.8 ft and weighing around 30-45 lbs.
Sources
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Velociraptor
- https://paleobiodb.org/classic/basicTaxonInfo?taxon_no=38564
- https://digitallibrary.amnh.org/bitstream/handle/2246/3223//v2/dspace/ingest/pdfSource/nov/N0144.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
- https://besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/2041-210X.12226
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/344034218_The_accuracy_and_precision_of_body_mass_estimation_in_non-avian_dinosaurs
Article last fact checked: Joey Arboleda, 06-08-2023
Featured Image Credit: Copyright (c) Thedinosaurs.org
