The Abelisaurus is a dinosaur with a name which translates to “Abel’s lizard.” Above all, it is a captivating figure from the annals of prehistoric life. Hailing from the Late Cretaceous period, it has intrigued scientists and dinosaur enthusiasts alike due to the mystery that surrounds it. Known primarily from a single, incomplete skull found in Argentina, the Abelisaurus presents a tantalizing puzzle for paleontologists.
Much like the infamous Tyrannosaurus Rex, the Abelisaurus was a bipedal carnivore. However, without its complete skeleton, much of its physical characteristics and behaviors are left to educated speculation. Despite these uncertainties, the Abelisaurus remains a fascinating subject of study, offering glimpses into a prehistoric world that continues to captivate our curiosity.
Key Facts
| Keyword | Fact |
|---|---|
| Abelisaurus pronunciation | ah-bel-i-sawr-us |
| Meaning of name | Abel’s lizard |
| Group | Abelisauridae |
| Type Species | Abelisaurus comahuensis |
| Diet | Carnivore |
| When it Lived | 83.5 to 70.6 MYA |
| Period & Time | Late Cretaceous |
| Epoch | Early/Lower Campanian to Middle Campanian |
| Length | 29.2 to 36.3 ft |
| Height | 6.5 ft |
| Weight | 2.5 to 3.3 tons |
| Mobility | Bipedal |
| First Discovery | 1983 by Roberto Abe |
| Location of first find | Anacleto Formation, Rio Negro Province, Argentina |
| First Described by | 1985 by José Bonaparte and and Fernando Emilio Novas |
| Holotype | MC 11078 |
Abelisaurus Origins: Taxonomy, Timeline, and Discovery
This dinosaur was named after Roberto Abel who discovered the first specimen and is a member of the Abelisauridae family–a group of carnivorous dinosaurs that thrived during the Cretaceous period. The only known species of this genus is Abelisaurus comahuensis, a tribute to the Comahue region of Argentina where the fossil was found.

It lived during the Late Cretaceous period, specifically around 80 million years ago. This places it in the Campanian stage of the Cretaceous, a time when the continents were slowly taking on their modern forms and the age of dinosaurs was nearing its end.
The first specimen was discovered in 1983 in the Anacleto Formation of the Rio Negro Province, Argentina. The discovery was made by Roberto Abel, the then director of the Provincial Museum of Cipolletti in Argentina. This incomplete skull was later described and named by Argentine paleontologists José Bonaparte and Fernando Emilio Novas in 1985.
Listen to Pronunciation
Fossil Evidence
Meanwhile, fossil evidence for the Abelisaurus is limited to a single, incomplete skull that is missing several key components–including the lower jaws and most of the palate. Despite these missing pieces, the skull measures over 85 centimeters long, providing a tantalizing glimpse into the size and structure of this prehistoric predator.

The lack of additional fossil evidence makes it challenging to draw definitive conclusions about Abelisaurus. However, the discovery of this single skull has sparked significant interest and research into the Abelisauridae family and led to the discovery of other related dinosaurs in the same region.
Abelisaurus Size and Description
The Abelisaurus stands out as a fascinating creature in the realm of dinosaurs.As a theropod, it is known for its bipedal nature, walking on two legs with a long tail that provided balance and stability. Its head was relatively short but it boasted powerful jaws, which is a typical characteristic of a carnivorous dinosaur.
Short description of Abelisaurus
The Abelisaurus, with its bipedal stance and balancing tail, is a quintessential theropod. Its relatively short head and powerful jaws were likely instrumental in its predatory lifestyle. It is believed that the Abelisaurus bore a striking resemblance to the Tyrannosaurus, another well-known theropod of the Cretaceous.
Size and Weight of Type Species
The size of the Abelisaurus can vary across different sources due to the limited fossil evidence available. The only known fossil of Abelisaurus is a partial skull, which makes it challenging to provide a reliable size estimate. In spite of this, several paleontologists have attempted to estimate its size based on this partial skull and comparisons with other abelisaurids.
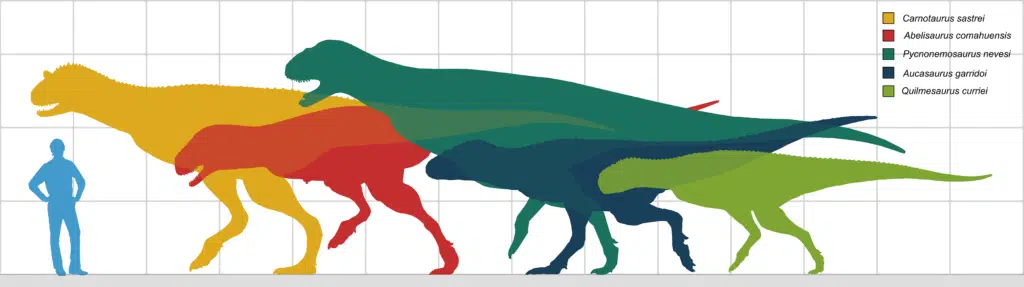
In 2010, Gregory S. Paul estimated the body length of Abelisaurus to be around 32 ft 10 in and its weight to be around 2.5 tons based on the assumption that abelisaurids have relatively short heads. In 2012, Thomas Holtz suggested a possible length of 36.3 feet, which is slightly larger than Paul’s estimate.
However, a comprehensive analysis done in 2016 of abelisaur size estimated the length of Abelisaurus to be 24 ft 3 inches. In the same year, the published paper by Rubén Molina-Pérez and Asier Larramendi gave a similar size estimate of 23.6 feet and a weight of 1.82 tons. These estimates are considerably smaller than the ones provided by Paul and Holtz.
Given these different results, an overall estimate based on the averages would place the length of Abelisaurus at around 29.2 feet and its weight at around 2.5 tons. However, it’s important to note that these are just estimates and the actual size of Abelisaurus could have varied. In order to provide a more accurate size we would need more fossil evidence.
The Ultimate Dino Quiz
Do you want to test your knowledge of dinosaurs? Then try this Ultimate Dino Quiz! Don’t worry if you get some of the answers wrong, and look at it as an opportunity to refresh and improve your knowledge!
Don’t forget to try our other games as well!
The Abelisaurus in Detail
The Abelisaurus was a medium-sized carnivorous dinosaur and a fascinating creature that has intrigued professionals and enthusiasts alike. Its physical characteristics, though largely deduced from a single incomplete skull, paint a picture of a formidable predator that once roamed the earth.
It was a typical bipedal theropod, meaning it walked on two legs with a long tail that provided balance and stability. It likely had a short head compared to its body size and the powerful jaws typical of a meat-eating dinosaur. This dinosaur, with its robust physical features, was undoubtedly a force to be reckoned with in its time.
The Abelisaurus in its Natural Habitat and Environment
The Abelisaurus lived in the Late Cretaceous Period in what is now known as Patagonia, Argentina. The environment during this time was diverse, with a variety of vegetation and many other dinosaur species cohabiting the same space. The Abelisaurus, with its carnivorous diet, would have been a top predator in this environment.
As a carnivore, the Abelisaurus would have preyed on other dinosaurs. One dinosaur expert, Gregory S. Paul, suggests that Abelisaurus preyed on Titanosaurians. Titanosaurs were huge sauropod dinosaurs that had long necks and tails and supported their massive size on all four legs. This group was related to giants such as Apatosaurus and Diplodocus. The Abelisaurus, with its powerful jaws and robust body, would have been well-equipped to hunt these large herbivores.
Like other theropods, the Abelisaurus was likely a solitary hunter. Its size and strength would have allowed it to take down large prey on its own. As of yet, much about the social behavior and life expectancy of the Abelisaurus remains unknown due to the limited fossil evidence available.
Fascinating Details about Abelisaurus
- Despite the lack of a complete skeleton, paleontologists have been able to infer a great deal about its size, appearance, and behavior from this lone specimen.
- Most importantly, the name of this dinosaur pays tribute to Roberto Abel, the discoverer of the type specimen and the former director of the provincial Museum of Cipolletti in Argentina. The name also incorporates the Greek word “sauros,” meaning ‘lizard’.
- For instance, belisaurus belongs to the Abelisauridae family, a group of dinosaurs known for their short arms and strong legs. Although Abelisaurus itself does not have bony crests or horns, it may have had some kind of crest made out of keratin, which would not have fossilized.
- This creature lived during the Late Cretaceous Period, a time when South America was an isolated continent. Above all, this isolation led to the evolution of a unique dinosaur fauna, including the abelisaurids.
- For instance, any believe that the Abelisaurus has been a top predator in its ecosystem.
Contemporary Dinosaurs to Abelisaurus
The Abelisaurus might have found a rival in the Aucasaurus. Both theropods, they were likely competitors whose survival hinged on the same resources. The Carnotaurus, another theropod, was smaller but faster; its agility possibly gave it an edge in the chase for prey. These interactions were a blend of competition and coexistence and would have shaped the dynamics of their shared habitat.
Yet, not all contemporaries were competitors. The Dreadnoughtus, a titan among dinosaurs, towered over the Abelisaurus. Its size, however, was not a threat but rather a show of the diversity of life during this period. This herbivore, focused on the abundant plant life, would have been largely indifferent to the Abelisaurus–except perhaps when defending its young.
The Secernosaurus was a smaller herbivore that presents an interesting contrast to the Dreadnoughtus and might have been a potential prey for the Abelisaurus. This dynamic where one creature’s survival depends on the other’s displays the interconnectedness of life in this prehistoric world. Through this lens, we can begin to appreciate the Abelisaurus not just as an individual species. Instead it was a key player in a vibrant and diverse ecosystem.
FAQs
Its name means “Abel’s lizard,” and it was named after Roberto Abel.
Our knowledge is limited as we know from only one partial skull. However, this has provided valuable insights into its size, appearance, and behavior.
It was a carnivore, which suggests that it may have hunted large sauropod dinosaurs.
Its estimated length varies from 29.2 to 36.3 ft, although this is uncertain due to the incomplete nature of the fossil record.
Above all, what makes this dinosaur unique is that it was the first named member of the Abelisauridae family, a group of dinosaurus known for having short arms, strong legs, and distinctive head crease or horns.
To clarify, the dinosaur was discovered in the nacleto Formation, Rio Negro Province, Argentina.
Sources
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Abelisaurus
- https://paleobiodb.org/classic/basicTaxonInfo?taxon_no=53946
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/237714676_ABELISAURUS_COMAHUENSIS_N_G_N_SP_CARNOSAURIA_FROM_THE_LATE_CRETACEOUS_OF_PATAGONIA
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/308792335_Records_y_curiosidades_de_los_dinosaurios_teropodos_y_otros_dinosauromorfos
The information in this article is based on various sources, drawing on scientific research, fossil evidence, and expert analysis. We aim to provide a comprehensive and accurate overview of the dinosaurs. However, please be aware that our understanding of dinosaurs and their world is constantly evolving as new discoveries are made.
This article was last fact checked: Joey Arboleda,06-08-2023
Featured Image Credit: Jordan Mallon, CC BY-SA 2.5, via Wikimedia Commons
