Let’s embark on a journey back in time to the Late Cretaceous Period where the enigmatic Secernosaurus roamed the ancient landscapes. This herbivorous dinosaur, whose name intriguingly means “Separated Lizard,” offers a fascinating glimpse into a world long gone. Discovered in the windswept formations of Argentina, Secernosaurus bridges the gap between the past and present and invites us to explore its life and times.
In this exploration, we’ll delve into the key aspects of Secernosaurus–from its discovery and physical characteristics to its natural habitat and the ecosystem it thrived in. Our journey will not only illuminate the life of this unique dinosaur but also shed light on the broader context of the Cretaceous Period.
Secernosaurus Key Facts
| Keyword | Fact |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | see-ser-noh-sore-us |
| Meaning of name | Separated Lizard |
| Group | Ornithopod |
| Type Species | Secernosaurus koerneri |
| Diet | Herbivore |
| When it Lived | 83.6 to 66.0 MYA |
| Period | Late Cretaceous |
| Epoch | Campanian to the top of the Maastrichtian |
| Length | 13.0 to 16.0 feet |
| Height | Approximately 5.0 feet |
| Weight | 700.0 to 800.0 pounds |
| Mobility | Moved on two legs |
| First Discovery | 1923 by J. B. Abbott |
| Described by | 1979 by Brett-Surman |
| Holotype | FMNH P13423 |
| Location of first find | Lago Colhué Huapi, Argentina |
Secernosaurus Origins, Taxonomy and Timeline
The name Secernosaurus translates to “Separated Lizard” from Latin and Greek, hints at its unique place of origin. Argentina is far from the typical Hadrosaur discovery sites in Eurasia and North America. This Ornithopod belongs to this Hadrosaurid family.
Taxonomically, this dinosaur is a fascinating subject. As a member of the Ornithopod group and the Hadrosaurid family, it showcases the diversity and adaptability of herbivorous dinosaurs. Its type species, Secernosaurus koerneri, is the only species in the genus and stands as a testament to its unique evolutionary path.
The timeline of this dinosaur spans the Campanian to Maastrichtian Epochs of the Late Cretaceous Period, approximately 83.6 to 66.0 million years ago. This era marks a significant chapter in Earth’s history, teeming with diverse life forms and dramatic environmental changes.
Listen to Pronunciation
Discovery & Fossil Evidence of Secernosaurus
The journey to understanding Secernosaurus began with the collection of its holotype in 1923, during an expedition led by J. B. Abbott for the Field Museum. This partial skeleton was unearthed from the Lago Colhué Huapi Formation in Chubut province, Argentina. However, it wasn’t until the 1970s that this specimen received the attention it deserved. In 1979, a significant milestone was reached when Brett-Surman formally named this species Secernosaurus koerneri.
This journey through scientific classification has been intriguing. A debate emerged in 2010 when Albert Prieto-Marquez and Guillermo Salinas proposed that Kritosaurus australis, another Hadrosaurid species, was synonymous with Secernosaurus koerneri. However in 2015, Rodolfo Coria observed differences between the two, casting doubt on this synonymy and suggesting a need for reevaluation. This taxonomic puzzle saw a significant development in 2022 when the two species were finally recognized as separate entities. Consequently, the genus Huallasaurus was established for Kritosaurus australis, clarifying the distinct identity of Secernosaurus koerneri.
This journey of discovery and classification highlights the dynamic nature of paleontological research. Each fossil find and subsequent study not only adds to our understanding of individual species like Secernosaurus but also enhances our knowledge of the broader dinosaur world. As we continue to uncover and study more fossils, our perception continues to evolve in order to offer us a richer, more nuanced picture of life millions of years ago.
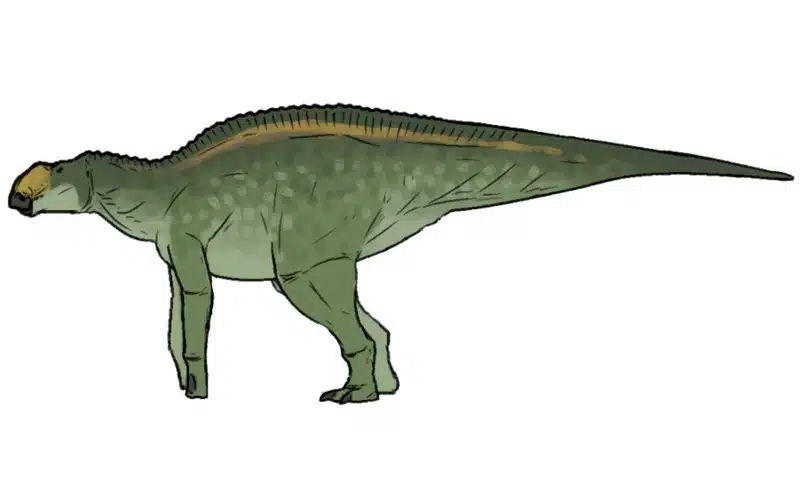
Secernosaurus Size and Description
This herbivore is a captivating subject within the realm of paleontology and presents a unique case in terms of its physical dimensions and overall appearance. Belonging to the Hadrosaurid family, it likely exhibited typical features of this group. Its characteristics provide insights into its lifestyle and adaptations–let’s take a closer look at them.
Size and Weight of Type Species

In terms of size, it may have been on the smaller side for a Hadrosaurid. The type specimen is central to our understanding of this species and indicates an individual approximately 13.0 to 16.0 feet long. Initially, this specimen was thought to represent a subadult. However, more recent interpretations suggest that it might have been more mature than previously believed. This reevaluation implies that the size range of 13.0 to 16.0 feet could be closer to the average for mature individuals of the species. In terms of weight, while specific figures are not available, the size estimates suggest a relatively lighter weight compared to larger Hadrosaurids. This smaller stature might have influenced its behavior and ecological role, possibly affecting its mobility, feeding habits, and interactions with other species and the environment.
The Dinosaur in Detail
Secernosaurus stands out for several reasons. Its unique evolutionary lineage, as indicated by its South American origin, sets it apart from its contemporaries. This distinction may reflect specific adaptations that allowed it to thrive in the ecosystems of the Late Cretaceous.
One of the most intriguing aspects of this herbivore is its bipedal locomotion. The limbs of this dinosaur suggest it was primarily bipedal, capable of moving efficiently on two legs. This mode of movement, coupled with its diet, suggests a lifestyle centered around efficient foraging and perhaps even social behaviors akin to other Hadrosaurids.
It probably had a robust body, a long, powerful tail, and a distinctively shaped head with a duck-bill-like snout. While the exact details of its skin texture are unknown, it’s plausible that, like many of its contemporaries, it had scaly skin. The limited fossil record of Secernosaurus leaves much to the imagination, yet it also opens doors to numerous hypotheses about its life and behavior. Each fragmentary fossil is a piece of the puzzle, contributing to our evolving understanding of this unique dinosaur.
Interesting Points about Secernosaurus
- Its name, meaning “Separated Lizard,” reflects its unique geographic origin, distinct from the Laurasian landmass.
- It was one of the few dinosaurs discovered in the southern hemisphere, offering a rare glimpse into Gondwanan dinosaur fauna.
- Its bipedal locomotion sets it apart from many of its contemporaries, suggesting a unique adaptation and foraging strategy.
- Despite its fragmentary fossil record, it plays a crucial role in understanding the diversity and distribution of Late Cretaceous herbivores.
- The discovery of Secernosaurus in Argentina sheds new light on the global distribution of the Hadrosaurid family and expands our knowledge of dinosaur ecology.
Secernosaurus in its Natural Habitat
This unique Hadrosaurid inhabited the region now known as Patagonia during the Maastrichtian Age of the Late Cretaceous Period. This South American dinosaur’s presence in South America, particularly in Patagonia, is a testament to the dynamic geological and ecological changes of that era. Its arrival in this part of the world is believed to be the result of a significant dispersal event from North America during the Campanian. This migration possibly occurred via a chain of islands formed by the proto-Antilles, allowing the movement of land vertebrates between the two continents. The introduction of Hadrosaurids like Secernosaurus into South America may have contributed to the decline of native Ornithopods, particularly the Elasmarians, introducing a notable shift in the ecological balance.

Initially, the area where Secernosaurus lived was characterized by fluvial systems and floodplain environments. This suggests a habitat with abundant water sources that supported a diverse array of plant life, which would have been crucial for a herbivore like Secernosaurus. However, the lower parts of the formation where Secernosaurus fossils were found also show evidence of semi-arid conditions. Large gypsum deposits and desiccation cracks indicate periods of intense aridization, contrasting sharply with the very humid climate of the earlier Bajo Barreal Formation.
Highly adaptable to its environment
Interestingly, palynological (pollen and other microfossil) data indicates that towards the end of the Cretaceous and into the Danian Age of the Paleocene, the climate in the region where Secernosaurus lived became milder, with a balance of wet and dry seasons. It is from these uppermost deposits of the formation that Secernosaurus fossils have been recovered. This suggests that it was well-adapted to a changing environment and capable of thriving in both humid and semi-arid conditions.
The habitat of Secernosaurus, therefore, was a dynamic and evolving landscape marked by shifts from lush floodplains to arid regions and back to a more balanced climate. This adaptability to varying environmental conditions might have been a key factor in the survival and evolution of Secernosaurus in the Late Cretaceous of South America.
Contemporary Dinosaurs
As a medium-sized herbivore, Secernosaurus often found itself in a delicate balance with its contemporaries. Among them was the smaller and more nimble Talenkauen. These two were not direct competitors due to their size difference but often grazed the same areas. Imagine Secernosaurus, ambling through the prehistoric foliage with its sturdy build while Talenkauen darted around. Both could feast on the abundant plant life, always mindful of each other’s presence.
Similar in size and shape to Secernosaurus was Huallasaurus. These two herbivores would have spent much time in direct competition with each other, both constantly fighting for the finest food. Not much is known about Huallasaurus, but we can imagine that must have found some way to exist alongside Secernosaurus in peace.
Gasparinisaura, a swift-moving herbivore, often found itself in the periphery of Secernosaurus’s world. While not a direct competitor or threat, its presence added to the dynamic environment Secernosaurus inhabited. Imagine Gasparinisaura darting between the legs of the larger dinosaurs, a small but significant part of the ecosystem, contributing to the intricate web of relationships that defined Secernosaurus’s existence.
Frequently Asked Questions
The name translates to “Separated Lizard,” reflecting its unique evolutionary lineage and geographic origin separate from its relatives.
It roamed the Earth during the Late Cretaceous Period, approximately 83.6 to 66.0 million years ago.
It was an Ornithopod, part of the Hadrosaurid family, known for being herbivorous and often bipedal.
The first fossils were discovered in the Lago Colhué Huapi and Los Alamitos formations in Argentina in 1923.
While exact measurements are speculative, Secernosaurus is believed to have been a medium-sized dinosaur.
Secernosaurus primarily moved on two legs, as suggested by its limb structure and overall body plan.
Sources
The information in this article is based on various sources, drawing on scientific research, fossil evidence, and expert analysis. The aim is to provide a comprehensive and accurate overview of Secernosaurus. However, please be aware that our understanding of dinosaurs and their world is constantly evolving as new discoveries are made.
Article last fact-checked: Joey Arboleda, 01-16-2024
Featured Image Credit: Connor Ashbridge, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
