The herbivore Tsintaosaurus lived during the Late Cretaceous period. This dinosaur, whose name translates to “Qingdao lizard,” has an appearance that makes it an interesting source of study. These unique features and the mysteries surrounding its existence make it a captivating topic to delve into.
Key facts
| Keyword | Fact |
|---|---|
| Tsintaosaurus pronunciation | ching-dow-sore-us |
| Meaning of name | Qingdao lizard |
| Group | Ornithopod |
| Type Species | Tsintaosaurus spinorhinus |
| Diet | Herbivore |
| When it Lived | 83.6 to 72.1 MYA |
| Period | Late Cretaceous |
| Epoch | Campanian |
| Length | 32.8 ft |
| Height | 12.1 ft |
| Weight | 2.6 tons |
| Mobility | Moved on all four |
| First Discovery | 1950 by C.C. (Chung Chien) Young |
| Location of first find | Tsingtao, Shandong Province |
| First Described by | 1958 by C.C. (Chung Chien) Young |
| Holotype | IVPP AS V725 |
Tsintaosaurus Taxonomy and Timeline

The name Tsintaosaurus, pronounced as “ching-dow-sore-us,” is derived from the location of its fossil discovery, Tsingtao, and the Greek word “sauros,” meaning reptile or lizard. This dinosaur is a testament to the rich biodiversity that existed during the Late Cretaceous period–particularly in what is now known as the Shandong Province of China.
Belonging to the Ornithopoda group, Tsintaosaurus is a part of the Hadrosauridae family. This family is often referred to as “duck-billed dinosaurs” due to the distinctive shape of their snouts. The type species of our focus is Tsintaosaurus spinorhinus, a unique member of this family.
The timeline of this herbivorous dinosaur puts it in the Late Cretaceous period, specifically the Campanian epoch. This places its existence in a time when dinosaurs were at the peak of their evolution before their inevitable downfall.
Listen to Pronunciation
Discovery & Fossil Evidence
The first discovery of Tsintaosaurus fossils were made in 1950 by the renowned Chinese paleontologist C. C. Young. The location of this significant find was near Tsingtao, in the Shandong Province of China. Young went on to describe the dinosaur in 1958, marking a significant contribution to our understanding of the Hadrosaurid family.

The holotype, labeled IVPP AS V725, was found in a layer of the Jingangkou Formation. It consists of a partial skeleton and skull that provide valuable insights into the physical characteristics of this dinosaur. Additional partial skeletons and a large number of disarticulated skeletal elements were also found in the same area, further unearthing the mysteries of this dinosaur.
Tsintaosaurus Size and Description
Tsintaosaurus was a member of the Hadrosauridae family which are often referred to as “duck-billed dinosaurs” due to the distinctive shape of their snouts. It was a quadrupedal dinosaur, meaning it moved on all four legs although it was also capable of bipedal locomotion. This flexibility allowed it to feed at varying heights and increased the range of plants it could consume.
Its most distinctive feature was its forward-pointing crest, a feature that initially sparked debate among paleontologists. However, the discovery of additional specimens with the same crest placement confirmed that this was indeed a natural feature of the Tsintaosaurus. The crest was hollow, a characteristic that classifies the Tsintaosaurus as a lambeosaurine hadrosaurid.

Size and Weight of Type Species
This was a sizable dinosaur with an estimated length of up to 33 feet, a height of 10-12 feet and a weight in the range of 2.5 US tons. However, it’s important to note that these estimates are based on the available fossil evidence and actual sizes could have varied.
The Dinosaur in Detail
Tsintaosaurus was a unique dinosaur, boasting a set of features that set it apart from its contemporaries. The most distinctive of these was its forward-pointing crest, a feature that initially sparked debate among paleontologists. However, the discovery of additional specimens with the same crest placement confirmed that this was indeed a natural feature of Tsintaosaurus. The hollow nature of the crest suggests it may have been used for a variety of purposes, such as communication or display.
Its ability to move both bipedally and quadrupedally is another notable feature. This flexibility allowed it to feed at varying heights, increasing the range of plants it could consume. This adaptability likely played a significant role in its survival during the Late Cretaceous period.
Tsintaosaurus in its Natural Habitat
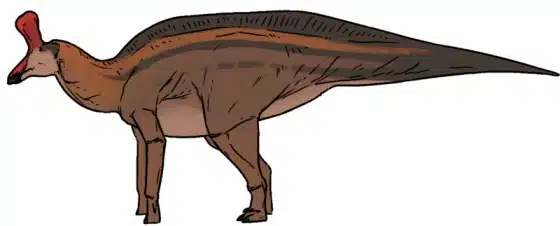
During the Late Cretaceous period, the environment was likely lush and verdant with a wide variety of vegetation that this herbivore would have fed on. Because it had the ability to rear up bipedally onto its back legs, it would have been able to feed on a wide range of vegetation.
It was likely a social animal that lived in herds for protection and to increase its chances of finding food. Its distinctive crest may have played a role in communication within the herd, possibly serving as a visual signal or even producing sounds.
This sizable herbivore would have likely played a significant role in shaping the landscape around it. Its feeding habits would have influenced the vegetation and its movement could have affected the soil and waterways. Its existence was an integral part of the ecosystem of the Late Cretaceous period.
Interesting Points about Tsintaosaurus
- Its forward-pointing crest was initially a subject of debate among paleontologists because some speculated that it was a result of the fossilization process. However, the discovery of additional specimens with the same crest placement confirmed that this was indeed a natural feature of the Tsintaosaurus.
- It was a member of the Hadrosauridae family which are often referred to as “duck-billed dinosaurs” due to the distinctive shape of their snouts. Its hollow crest placed it in the Lambeosaurinae group.
- This was a sizable dinosaur with estimates suggesting it could reach up to 10 meters in length. Its weight is still unknown due to limited fossil evidence.
- It was capable of both bipedal and quadrupedal locomotion, reflecting its adaptability in different environments.
- It lived during the Late Cretaceous period, specifically the Campanian epoch, a time when the Earth was teeming with diverse life forms.
Contemporary Dinosaurs
This Chinese dinosaur coexisted with an intriguing array of contemporaries. Among these were Hadrosaurus, Pinacosaurus, and Troodon, each contributing to the intricate dance of survival in their shared environment and shedding light on the life of the contemporary Tsintaosaurus.
A fellow herbivore and relative, Hadrosaurus was considerably larger than Tsintaosaurus. Despite this size difference, they likely grazed side by side in competition for the abundant vegetation of their shared habitat. The presence of Pinacosaurus, a sturdy, armored herbivore, might have added an element of caution to Tsintaosaurus‘ daily routine. The formidable defenses of this contemporary made it no easy prey for predators, possibly influencing the hunting patterns of carnivores in the region and indirectly affecting Tsintaosaurus‘ survival strategies.
Troodon, a smaller but agile carnivore, presents an intriguing contrast. Its presence might have posed a threat to Tsintaosaurus, especially to the young or weak. Tsintaosaurus, with its long, slender build and distinctive crest, would have had to rely on its keen senses and swift legs to evade such predators. This dynamic interplay of survival, competition, and coexistence paints a vivid picture of Tsintaosaurus‘ life and sheds light on its existence within the rich, complex ecosystem of its time.
List of All Dinosaurs
We have created a list of all dinosaurs we have covered here, sorted across the seven main groups of dinosaurs. We also include information about their type of diet, (omnivore, herbivore or carnivore) and the time they lived.
Frequently Asked Questions
The name translates to “Qingdao lizard,” derived from the location of its fossil discovery, Tsingtao, and the Greek word “sauros,” meaning reptile or lizard.
It was an herbivore, feeding on the variety of vegetation present during the Late Cretaceous period.
The Tsintaosaurus was capable of both bipedal and quadrupedal locomotion, allowing it to adapt to different environments and feeding situations.
Its most distinctive feature is its forward-pointing crest, a feature that was confirmed to be a natural part of the dinosaur through the discovery of additional specimens.
The first discovery of remains was made in 1950 by the renowned Chinese paleontologist C. C. Young.
It lived during the Late Cretaceous period, specifically the Campanian epoch, around 83.6 to 72.1 million years ago.
Sources
- https://www.chinascientificbooks.com/palaeontologia-sinica-new-series-cwhole-number-142no16the-dinosaurian-remains-of-laiyang-shantung-p-3969/
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/02724634.2017.1289381
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/316776736_Review_of_historical_and_current_research_on_the_Late_Cretaceous_dinosaurs_and_dinosaur_eggs_from_Laiyang_Shandong
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/292888523_Hadrosaurs_from_the_far_east_Historical_perspective_and_new_amurosaurus_material_from_blagoveschensk_amur_region_Russia
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/258405977_New_Material_and_Phylogenetic_Position_of_Arenysaurus_ardevoli_a_Lambeosaurine_Dinosaur_from_the_Late_Maastrichtian_of_Aren_Northern_Spain
Please note that the information in this article is based on various sources, drawing on scientific research, fossil evidence, and expert analysis. The aim is to provide a comprehensive and accurate overview of Tsintaosaurus, but please be aware that our understanding of dinosaurs and their world is constantly evolving as new discoveries are made.
This article was last fact checked: Joey Arboleda, 06-13-2023
Featured Image Credit: Nobu Tamura, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
