The world of dinosaurs is vast and varied with creatures of all shapes and sizes. One such dinosaur, Psittacosaurus, is a fascinating specimen from the Early Cretaceous period. This dinosaur is known as the “parrot lizard”. Named for its distinctive beak-like mouth, similar to that of a modern-day parrot. In this article, we delve into the intriguing world of Psittacosaurus and explore its origins, discovery, and the environment it once roamed.
Psittacosaurus Key Facts
| Keyword | Fact |
|---|---|
| Psittacosaurus pronunciation | SIT-ak-oh-sore-us |
| Meaning of name | Parrot Lizard |
| Group | Ceratopsians |
| Type Species | Psittacosaurus mongoliensis |
| Diet | Herbivore |
| When it Lived | 139.8 to 99.6 MYA |
| Period | Early Cretaceous |
| Epoch | Valanginian to Late/Upper Albian |
| Length | 6.0 to 7.0 ft |
| Height | 1.6 to 2.6 ft |
| Weight | 40 lbs |
| Mobility | Moved on two legs |
| First Discovery | 1923 by a driver (named Wong) for an American Museum of Natural History expedition |
| Location of first find | Gobi Desert, Mongolia |
| First Described by | 1923 by Henry Fairfield Osborn |
| Holotype | AMNH 6254 |
| Also found in | China, Russia, and Thailand |
Psittacosaurus Taxonomy and Timeline
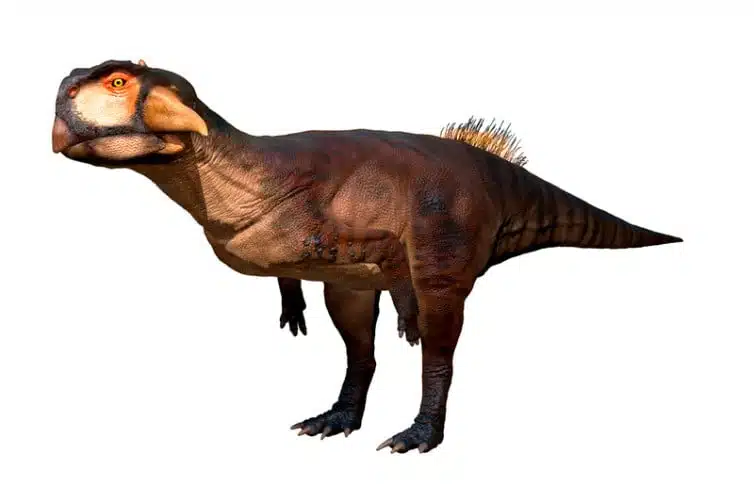

Psittacosaurus, or “Parrot Lizard,” gets its name from its distinctive beak-like mouth, which is reminiscent of a parrot’s beak. This unique feature sets it apart from many other dinosaurs and is a key characteristic of this fascinating creature. The name is derived from the Greek words ‘psittacus’ for parrot and ‘sauros’ for lizard.
In terms of taxonomy, Psittacosaurus belongs to the Ceratopsian group. This is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs that are characterized by their beaked mouths. Within this group, it is part of the Psittacosauridae family, which includes other similar dinosaurs. The species most commonly referred to when discussing this dinosaur is Psittacosaurus mongoliensis, although there are several other recognized species within the genus. It lived during the Early Cretaceous period, making it one of the earlier members of the Ceratopsian group.
Listen to Pronunciation
Discovery & Fossil Evidence
In 1923, Wong, a driver for an American Museum of Natural History expedition, unearthed the first fossils of Psittacosaurus in the Gobi desert, Mongolia. This region has since become renowned for its rich dinosaur fossil record. This dinosaur was first described by Henry Fairfield Osborn in the same year as its discovery.

The discovered specimen, known as AMNH 6254, served as the holotype for Psittacosaurus. Using a holotype, researchers provide a single physical example of an organism when formally describing a species. Furthermore, this holotype is frequently regarded as the “gold standard” for defining that species.
The AMNH 6254 specimen is housed at the American Museum of Natural History and serves as a tangible link to a creature that roamed the earth millions of years ago.
Over the years, numerous other fossils of this dinosaur have been found. With finds extending beyond the borders of Mongolia to China, Russia, and even Thailand. These additional finds have painted a more complete picture of Psittacosaurus and allowed scientists to piece together its physical characteristics, diet, and behavior with greater accuracy.
The fossils themselves have varied greatly in terms of their preservation and completeness. Some specimens represent almost complete skeletons that offer a wealth of information about the dinosaur’s physical structure. Others consist of partial skeletons or isolated bones, which, while less informative, still contribute valuable pieces to the puzzle.
Psittacosaurus Size and Description
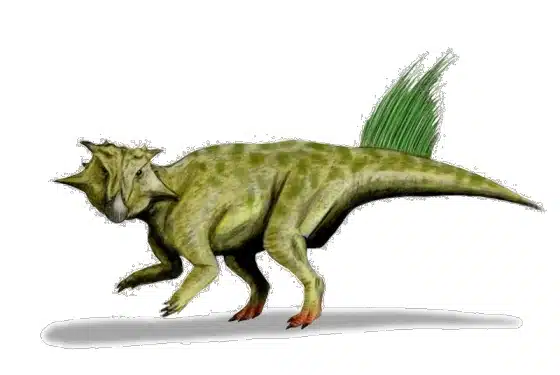
Psittacosaurus was a small to medium-sized dinosaur and characterized by its bipedal stance, long tail, and–most notably–its parrot-like beak. Its body was compact with a large head relative to its body size. The dinosaur’s neck was short and strong to support its large head. Its vertebrae were robust and provided a sturdy framework for its body.
It had strong hind limbs used for locomotion and smaller forelimbs, which were likely used for foraging and other tasks. Its tail was long and likely acted as a counterbalance when it was moving. The dinosaur’s skin was covered in scales, similar to modern reptiles.

Size and Weight of Type Species
The size of this dinosaur varied between different species, but on average, this dinosaur was about 6.0 to 7.0 feet long. It is estimated to have been around 1.6 to 2.6 feet tall. Weight estimates are less precise but it’s generally believed that this dinosaur weighed around 40 lbs.
The Dinosaur in Detail
Psittacosaurus is a dinosaur that stands out from the crowd thanks to a number of unique features. One of the most distinctive characteristics is its beak-like mouth. This feature, which gives the dinosaur its name of “Parrot Lizard” is not just a physical characteristic, but also a tool that likely played a crucial role in the dinosaur’s survival.
The beak was likely used for foraging and eating. Its sharp, pointed structure would have been ideal for breaking apart plant matter, allowing the dinosaur to access nutrients that other dinosaurs might not have been able to. This adaptability in diet could have given this herbivore a significant advantage in the competitive world of the Early Cretaceous.
Another feature that sets it apart from many other dinosaurs is its bipedal stance. While many Ceratopsians were quadrupedal and moved on all fours, this dinosaur was capable of moving on two legs. This bipedal locomotion would have given the dinosaur greater speed and agility, potentially allowing it to evade predators more effectively.
The soft tissue of this dinosaur is better known than most. It primarily had rough scales, but a line of bristle-like structures, likely made of keratin, ran along its back. Additionally, some samples revealed that it had striped or spotted coloration, reminiscent of modern animals in dense forests.
The extensive fossil record of Psittacosaurus has also contributed to our understanding of this dinosaur. Each offering new insights into the dinosaur’s physical characteristics, behavior, and environment. These fossils have allowed scientists to piece together a detailed picture of Psittacosaurus, making it one of the most well-understood dinosaurs from the Early Cretaceous period andamong non-avian dinosaurs in general.
The Psittacosaurus in its Natural Habitat
The herbivore Psittacosaurus lived in a variety of environments including forests, floodplains, and possibly even semi-arid regions. The climate during the Early Cretaceous was generally warm and there were likely a variety of plants available for the Psittacosaurus to eat.
As an herbivore, it would have fed on a variety of plants. Its beak-like mouth would have been well-suited to breaking apart plant matter. Moreover, it may have been able to eat a wider variety of plants than other herbivorous dinosaurs.
This was a bipedal dinosaur, meaning it moved on two legs. This would have given it a speed advantage over many other dinosaurs and allow it to more easily evade predators. It’s also possible that it lived in herds, which would have provided further protection from predators.
Interesting Points about Psittacosaurus
- This is one of the most extensively studied dinosaurs, thanks to its extensive fossil record.
- Despite being a Ceratopsian, the Psittacosaurus did not have the large frill or horns that characterize later members of this group.
- It has a line of bristle-like structures running along its back.
- The beak was not only used for eating. It likely played a role in its social interactions.
- It had a wide geographical distribution, with fossils found in several countries across Asia.
Contemporary Dinosaurs
In the lush, green world of the early Cretaceous period, our main dinosaur navigated a complex web of relationships with its contemporaries. Picture a bustling prehistoric landscape where the Psittacosaurus, with its parrot-like beak, roamed alongside the Hongshanosaurus, Chaoyangsaurus, and Yinlong. Each of these Asian dinosaurs were unique players in the grand theater of life in the Early Cretaceous.
The herbivorous Psittacosaurus was roughly the same size as Chaoyangsaurus, another plant-eater. They likely competed for the same resources, their paths crossing in a dance of survival as they grazed on the same ferns and cycads. Yet, despite this competition, they coexisted–their interactions more a gentle waltz than a fierce tango. The smaller and more elusive Yinlong was less of a competitor. Its diet consisted of different plant species, allowing it to exist in harmony with Psittacosaurus.
But life wasn’t all peaceful grazing for these herbivores. Hongshanosaurus, larger and more imposing, was a potential predator. However, Psittacosaurus was no easy prey despite its smaller size. It was swift and agile, its long legs carrying it swiftly across the landscape when danger lurked. The predator-prey relationship between Hongshanosaurus and Psittacosaurus added a thrilling edge to their coexistence–a constant game of cat and mouse that kept the ecosystem in balance.
In this vivid tableau of prehistoric life, Psittacosaurus was a central figure whose interactions with its contemporaries paint a rich picture of its existence. Through the lens of Psittacosaurus’s life, we glimpse the dynamic, ever-changing world of the early Cretaceous period–a world teeming with life, competition, and coexistence.
List Of All Dinosaurs
We have created a list of all dinosaurs we have covered here, sorted across the seven main groups of dinosaurs. We also include information about their type of diet, (omnivore, herbivore or carnivore) and the time they lived.
Frequently Asked Questions
The name means “Parrot Lizard,” a reference to its distinctive beak-like mouth. It has Greek origins.
It lived during the Early Cretaceous period between 139.8 to 99.6 million years ago.
The Psittacosaurus was an herbivore, meaning it ate plants.
It was a small to medium-sized dinosaur with an average length of about 6.0 to 7.0 feet and a height of about 1.6 to 2.6 feet.
Sources
The information in this article is based on various sources, drawing on scientific research, fossil evidence, and expert analysis. The aim is to provide a comprehensive and accurate overview of the Psittacosaurus. Our understanding of dinosaurs and their world constantly evolves with new discoveries. Please stay aware of these ongoing changes.
Article last fact-checked: Joey Arboleda, 07-23-2023
Featured Image Credit: Пётр Меньшиков, CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
